Notice: Undefined index: row in /home/ndc9e95/public_html/wp-content/themes/wholisticmatters/modules/basic-content.php on line 7
Understanding Types of Fat
Fat, along with carbohydrate and protein, constitutes a basic macronutrient component of food. However, not all fats are created equal. Understanding the differences between the various types of fat is key. There are different types of fat that have various health benefits associated with them.
As a macronutrient, fat promotes:
- Energy production
- Healthy skin and hair
- Fat-soluble vitamin absorption
- Body insulation
Saturated and Trans Fat
Saturated fats are those that are usually in a solid form at room temperature:
- Butter
- Palm and coconut oils
- Cheese
- Red meat1
High intake of these types of fat is often associated with heart disease risk and unhealthy weight gain. This is because high consumption of saturated fat raises levels of “bad” cholesterol, called low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
In 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration gave the food industry three years to remove all artificial trans fats from food products, declaring them unsafe.2 Trans fats are produced as a result of processing liquid oils into solid fats, a process called hydrogenation. Trans fats are found in:
- Fried and battered food
- Shortening and stick margarine
- Cakes, cake mixes, pies, pie crust3
Like saturated fats, trans fats raise levels of LDL cholesterol, and they reduce levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), also known as “good” cholesterol. Trans fats are associated with increased risk of heart diseases, weight gain, and stroke.
Unsaturated Fat
Unsaturated fat can be either mono-unsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) or polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). Oil sources of unsaturated fat are usually those that are liquid at room temperature:
- Olive and canola oil
- Safflower, sunflower, corn, and soy oil
MUFAs exist in vegetable oils, nuts, avocadoes, and other plant foods.[4] PUFAs are found in fish, vegetable oils, nuts and seeds, and some other animal and plant foods.5 Both MUFAs and PUFAs are associated with decreased risk of chronic diseases.6 Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are two different kinds of PUFAs, each with their own distinct health benefits. Omega-6 fatty acids include linoleic acid (LA) and arachidonic acid. Omega-3 fatty acids include alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
The Numbers: Fatty Acids
Download: Download PDF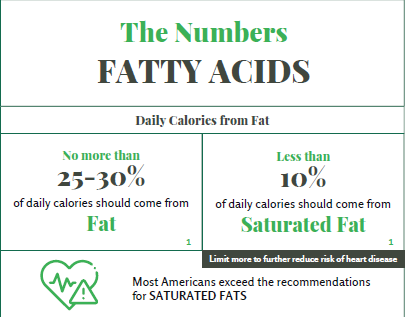
Unfolding Fatty Acids
Understand the difference between saturated and unsaturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated, as well as omega-6 versus omega-3 fatty acids. Download and print out your free copy.
Download: View PDF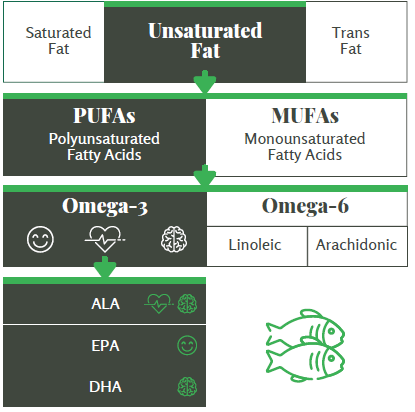
Notice: Undefined index: row in /home/ndc9e95/public_html/wp-content/themes/wholisticmatters/modules/basic-content.php on line 7
The Power of Omega-3s
Until 1929, scientists did not consider fatty acids like omega-3s to be much more than a source of calories.7 In a monumental report, George and Mildred Burr shone the first light on fatty acids as essential nutrients required to maintain health. Almost a century later, hundreds of studies on fatty acids and their role in human health make up a library of knowledge on these essential nutrients.
Fish oil as a source of omega-3 fatty acids is one of the most popular nonvitamin/nonmineral dietary supplements used by both adults and children.17 Omega-3 fatty acids are associated with reducing the risk of coronary heart disease, mental abnormalities, and developmental disorders.8-10
In the human body, the brain and retinas are loaded with omega-3 fatty acids (ALA, EPA, DHA), building the phospholipid structures of the cell membrane. Various functions of omega-3s include:
- Signal transduction11,12
- Energy source11,12
- Regulation of cardiovascular, pulmonary, immune, and endocrine systems9, 12-15
ALA is an essential fatty acid and is the precursor for both EPA and DHA. ALA must be obtained from the diet, as the body cannot make ALA on its own. ALA is associated with neuroprotection, vasodilation of arteries, and neuroplasticity.16 Dietary sources of ALA include fish/seafood and plant oils like flaxseed, soybean, and canola oils.17
EPA is associated with a positive effect on emotional balance.10,18 Just fifteen percent of ALA turns into EPA, and even a smaller amount is eventually converted to DHA.17 DHA is the most abundant omega-3 in the brain. It is a major component of the neuronal membrane and plays an important role in normal brain structure.
Both EPA and DHA are precursors for resolvins, molecules named for their role in resolving the inflammatory response.19 Specifically, some studies have shown that supplementation with EPA and DHA is associated with:
- Decreased markers of inflammation8,9
- Reduced risk of new blood vessel formation in the retina20
- Healthy cognitive function in elderly patients21
- Improved vascular preservation
- Reduced risk of heart disease22,23
A balanced dietary intake ratio of omega-6s and omega-3s reduces inflammatory activity and is associated with reduced risk of chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease and cancer.17 Although there is no clear consensus on the proper ratio of omega-6 to omega-3, it is prudent to ensure that the dietary intake of omega-6 to omega-3 ratio not exceed 4:1. Unfortunately, the intake ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 in the United States is estimated to be as high as 20:1.24
The National Academy of Medicine established adequate intake (AI) levels for omega-3 fatty acids as follows:17
According to 2011–2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data, the majority of children and adults in the United States consume recommended amounts of omega-3 fatty acids in the form of ALA but with low amounts of DHA and EPA.
While the average Western diet tends to favor saturated, monounsaturated, and omega-6 PUFAs, a lifestyle change with increased fish and seafood consumption, and supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids when needed can address suboptimal dietary intake of these key fatty acids.25 These lifestyle changes could tip the balance in favor of omega-3s, welcoming in the plethora of health benefits that accompany these fatty acids.
Adequate Intakes (AIs) for Omega-3s
Download: Download PDF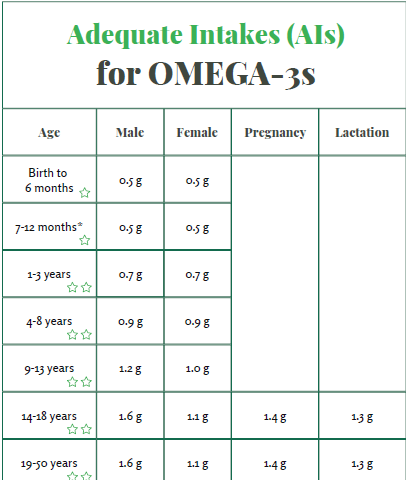
Notice: Undefined index: row in /home/ndc9e95/public_html/wp-content/themes/wholisticmatters/modules/basic-content.php on line 7
The Omega-3 Advantage for Heart Health
Poor nutrition is responsible for up to half of all deaths from heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes, which includes suboptimal intake of vital omega-3 fatty acids.27 Heart disease and diabetes costed the United States 650 billion dollars in 2003, a number that is expected to increase to 1.96 trillion dollars in 2023.28 Both MUFAs and PUFAs can improve metabolic parameters like blood pressure, lipid profiles, and insulin sensitivity. Both types of fat have also been studied to reduce inflammation, although the evidence base is stronger between reduced inflammation and PUFAs like omega-3 fatty acids. Addressing excessive inflammation is associated with a reduced risk of chronic conditions like heart disease and stroke.29-33
Omega-3 fatty acids are associated with reduced risk of heart disease due to their ability to support key functional systems. For example, increased intake of omega-3s has been shown to have anti-arrhythmic effects.8 EPA and DHA also help to lower triglyceride levels by reducing synthesis and secretion from the liver and can improve blood pressure by stimulating the dilation of small arteries.34
Additionally, EPA and DHA improve cardio-metabolic parameters in a few key ways:34
- Address plaque buildup in arteries by reducing levels of cytokines and adhesion molecule levels near the artery wall
- Increase size of LDL; as low LDL particle size is associated with risk for heart disease
- Reduce steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Increasing omega-3 fatty acid intake through dietary choices and/or supplementation can be effective at improving the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio. The more optimized the ratio, the more health benefits that can be gleaned, including improving cardio-metabolic parameters.34
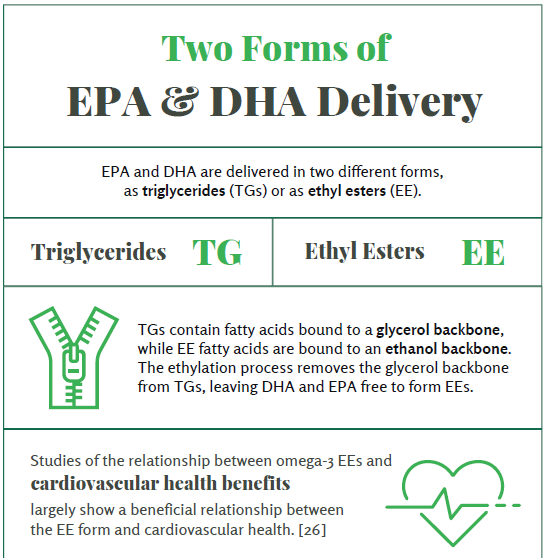
Two Forms of EPA & DHA Delivery
Download: Download PDF