Practitioner Resources
Empower your practice with clinically relevant, science-backed insights that inspire positive, transformational outcomes with your patients.
Explore our content across a diverse range of health and nutrition-related topics, patient concerns, and common clinical presentations.
Most Popular
Supporting Canine Cognitive Dysfunction: The Aging Dog Brain
Nancy Loes, DVM and Isabella Pulido
(10 min read)
As pets and people age, the accumulation of years is often accompanied by health challenges, both physically and cognitively. A multitude of factors influence the health of the brain and body over a lifetime, including genetics, lifestyle, environment, and nutrition. As dogs grow older, the cumulative effects of oxidative stress, inflammation, and nutritional deficiencies – often compounded by unstimulating or unhealthy environments – can contribute to memory impairment, reduced learning ability, and behavioral changes associated with cognitive decline.
Canine Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome (CCDS) is a commonly used term describing the behavioral manifestations associated with progressive cognitive decline in the canine patient. Other terms used include: “The Geriatric Condition,” “Sundowning (Sundowner’s Syndrome),”and “Doggie Dementia.”
The acronym DISHAA is often utilized as a tool to help pet owners and veterinary professionals identify the key signs of cognitive decline.6
The letters stand for:
D – Disorientation: Getting lost in what were once familiar places or stuck in corners, staring vacantly, exhibiting less reactive behaviors, and appearing to be puzzled by normal sights and sounds
I – Interactions (altered): Changes in social interactions with family members or other animals, which might include increased neediness, irritability, and/or personality changes
S – Sleep-wake cycle changes: A reversal of sleep-wake cycles, restless sleep and/or waking and wandering aimlessly at night
H – House soiling: A previously well house-trained dog may urinate or defecate in the house and/or exhibit deficits in other “learned” behaviors
A – Activity changes: Altered activity levels, such as a decrease in purposeful activity, disinterest in play, or (commonly noted) an increase in compulsive behaviors like pacing
A – Anxiety: Increased behavioral manifestations of anxiety, fear, and/or stress
Canine Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome (CCDS)
Pathogenesis
Late stages of CCDS are thought to be caused by the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques (outside neurons) and tau tangles (inside neurons) in the brain. These aggregates lead to neuroinflammation, neuronal loss, and synaptic dysfunction, all of which are similarly seen in Alzheimer’s disease. In addition to the combination of these mechanisms, synaptic impairment, myelin disruption, and glial cell activation are also thought to play critical roles in CCDS pathogenesis.5
A complex set of variables, signs of which may be subclinical, contribute to the pathogenesis and onset of CCDS, long before a dog reaches its senior years.
Proactive use of nutritional supplementation starting at an early age, particularly aimed at 1) encouraging robust blood flow, 2) promoting strong mitochondrial function and energy production, and 3) supporting healthy inflammatory processes, may attenuate or slow the accumulation of plaques and tangles, mitigate damage to the structure and function of the brain, and thus potentially delay both the onset and the progression of CCDS.
Prevalence and Breed Disposition
Studies suggest an estimated prevalence of 8.1% in dogs ages 8-11 years, 18.8% in ages 11-13, 45.3% in ages 13-15, and 67.3% in ages 15-17 years of age.5 There does not seem to be a breed predilection; however, many of these clinical signs have been more frequently reported in smaller dogs, possibly due to their tendency to live longer than their large-breed counterparts.
Diagnosis of Cognitive Dysfunction
The diagnosis of CCDS is based on behavioral signs reported by owners through questionnaires, requiring significant reliance on the pet owner’s ability to successfully identify and recall subtle behavioral changes. Taking recall bias into consideration, compounded with the absence of reliable biomarkers, CCDS is likely underdiagnosed.
Prevention / Management
Since aging is an inevitable process in life, prevention of CCDS focuses on delaying the onset of clinical signs and maintaining adequate quality of life. Because aging encompasses multiple physiological changes, a multimodal approach that combines nutritional and lifestyle modifications offers a comprehensive strategy for forestalling CCDS. Optimizing specific dietary components, such as essential omega fatty acids, B vitamins supportive of cognitive health, herbal support, and trophic nutrients can promote a high quality of life in an aging dog. Supplementation with antioxidant nutrients, energetic cofactors, and specific minerals can address potential nutritional deficiencies.1
Supplement Options to Address Canine Cognitive Dysfunction
While more research is needed to substantiate the best supplements for delaying and managing the onset of CCDS, here are a few compounds of interest with documented benefits.
Ginkgo biloba
Ginkgo biloba is an herbal supplement rich in flavonoids and terpenoids. Flavonoids are potent antioxidants that protect brain cells from oxidative stress and free radical damage, damage that is linked to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative conditions. The terpenoid, bilobalide, is noted for its neuroprotective effects and has been shown to protect neurons from damage, promote neuron survival, and support energy metabolism in brain cells.
Other active components of Ginkgo biloba are proanthocyanidins and quercetin, contributing to antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects.
Forty-two elderly dogs were enrolled in a study evaluating the effectiveness of a Ginkgo biloba dry leaf extract on behavioral disturbances commonly experienced by dogs over the age of 7 years.7
Results were determined by scores assigned to each clinical sign of cognitive decline (disorientation, sleep/activity changes, behavioral changes, general physical condition/vitality).
At a dose of 4 mg/kg for 8 weeks, Ginkgo biloba significantly reduced the severity of the “geriatric condition” in the dogs with a history of behavioral disturbances (p=0.0002).
Although statistical significance was not reached until 8 weeks, there was a noticeable difference in 4 weeks. All signs evaluated were significantly improved by the end of the study and at its conclusion, 36% of the dogs were completely free of the scored clinical signs of cognitive decline.
The combination of multiple bioactives in Ginkgo biloba work synergistically to provide cognitive benefits, such as reducing oxidative damage to brain cells, improving cerebral blood flow, modulating neurotransmitter activity, and protecting neurons from age-related damage.
These effects are believed to be the underpinnings for Ginkgo’s potential to enhance memory, improve cognitive function, and slow down cognitive decline, particularly in aging individuals or those with cognitive impairments.
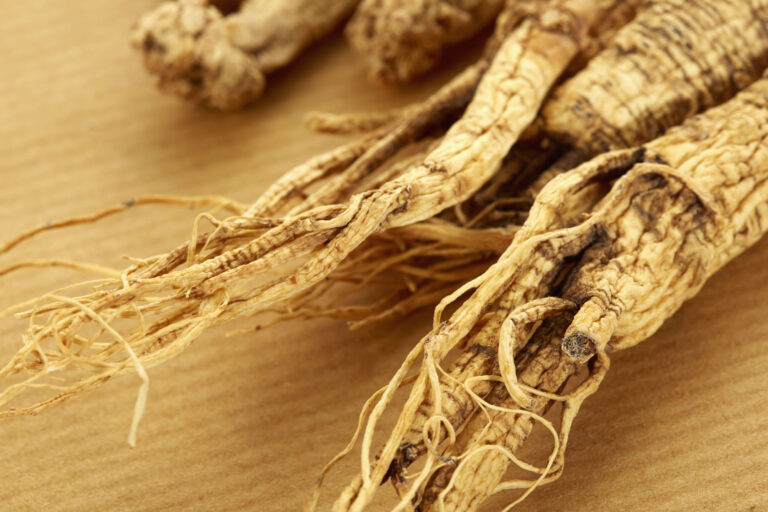
Panax ginseng root
The Panax ginseng root is rich in active compounds called ginsenosides, which contribute to its wide array of health benefits. Ginseng is often referred to as an adaptogen, a natural substance believed to help the body resist stressors of various kinds, whether physical, chemical, or biological.2
Health benefits from Panax ginseng include boosting energy levels, reducing inflammation, and supporting the immune system. In the brain, ginseng has immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties. Panax ginseng assists in keeping microglia cells (the primary immune cells of the central nervous system that operate as its defense, maintenance, and “clean-up” crews) in a healthy, anti-inflammatory state.
In a healthy state, microglia are highly dynamic, supporting neural circuits and brain function.
As age degeneration occurs, microglial cells (sometimes referred to as phagocytic neurons) may become stuck in a damaging positive feedback loop, inducing harmful cytokines, becoming proinflammatory, and eventually injuring microglial cells as well.
Ginseng can potentially prevent microglial cells from recruiting those harmful cytokines, thus reducing inflammation in the brain and enhancing cell survival.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
Coenzyme Q10, also known as ubiquinone/ubiquinol, is a fat-soluble compound that plays a vital role in brain health through a myriad of mechanisms including energy production, antioxidant activity, support for cellular health and the immune system, as well as the regeneration of antioxidants. While found naturally in the body, CoQ10 levels tend to decline with age, which may factor into Alzheimer’s-related mitochondrial dysfunction and the progression of CCDS.
CoQ10’s natural functions in the body, including its role in energy production and antioxidant properties, underscores how important this ingredient is for brain health and why supplementation is of benefit and recommended.
B Vitamins
B vitamins are coenzymes in a multitude of enzymatic processes that underlie almost every aspect of cellular functioning. Additionally, each of these B vitamins play a crucial role in brain health.
Thiamin (B1) is utilized as a neuromodulator in the acetylcholine neurotransmitter system and contributes to cellular membrane structure and function including neuroglia and neurons.3
Niacin (B3) works to modulate inflammatory cascades and participates in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, essential for communications between cells. It assists in the breakdown of fat, protecting against the development of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
Pantothenic Acid (B5) is the substrate for coenzyme-A which contributes to the structure and function of brain cells through its involvement in cholesterol, amino acid, phospholipid, and fatty acid synthesis.3 It is also involved in the synthesis of steroid hormones and multiple neurotransmitters.
Pyridoxine (B6) is a rate-limiting cofactor in the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), noradrenaline, and melatonin.
Folate (B9) is crucial for DNA synthesis and stability as well as cell division, processes that are critical for cognitive development and function. Folate is recommended during pregnancy to reduce the risk of birth defects of the spine (such as spina bifida, the spinal column doesn’t close properly) and brain (anencephaly, the brain and/or the skull don’t form properly). When there is a folate deficiency, neuronal differentiation and repair may be impacted leading to hippocampal atrophy, demyelination, and compromised phospholipid membranes upsetting the normal flow of nerve impulses.
Cobalamin (B12) protects myelin (the protective sheath around nerves) and is involved in neurotransmitter synthesis (including serotonin and dopamine, neurotransmitters that affect mood, memory, and focus). Along with folate (B9) and pyridoxine (B6), cobalamin (B12) also assists in breaking down homocysteine (high levels of homocysteine are linked to poor cognitive function and increased risk of cognitive decline).
With the simple addition of readily available B Vitamins, aging dogs stand to benefit enormously, physically and neurologically, on multiple fronts.
Beta-glucan
Beta-glucans are structural components in the cell walls of fungi (including mushrooms and yeast), cereal grains (such as oats), and bacteria that are clinically supported to promote immune system and gastrointestinal tract health.
Orally administered beta-(1,3)/(1,6)-glucans cause immunopotentiation, modulating both non-specific and specific immunity.
In a study in healthy dogs, 4 mg/kg mushroom beta-glucans were administered to 30 puppies (15 in treatment group) undergoing vaccination against rabies and canine parvovirus. Significant increases (p <0.001) in phagocytic activity of leukocytes were observed compared to the control group as well as protective titers were achieved earlier and reached higher levels than the control group.9
Organic Lion’s Mane (Hericium erinaceus) mushroom extract: In addition to beta-(1,3)/(1,6)-glucans, Lion’s Mane also contains powerful bioactive compounds such as the diterpenes, hericenones and erinacines.8 These compounds are thought to be responsible for the stimulation of nerve growth factor and brain derived neurotrophic factor, which assist in the prevention of neuronal death as well as the maintenance and repair of neurons.
Alpha-Glyceryl Phosphoryl Choline (Alpha-GPC)
Alpha-Glyceryl Phosphoryl Choline is a choline donor that can provide the choline required to produce an important neurotransmitter, acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine is crucial for energy regulation and utilization, influencing alertness, focus (motivation), and neuromuscular control, all energy-intensive processes.
Acetylcholine is integral to brain metabolism, especially in supporting neurons’ metabolic demands for functions including attention, memory, and learning.
Supplementation with Alpha-GPC allows more choline to reach the brain faster and more efficiently compared to standard supplementation of choline alone.
Both Alzheimer’s disease and CCDS are characterized by cholinergic hypofunction with reduced levels of acetylcholine.5 Alpha-GPC supplementation is recommended towards enhancing production of the acetylcholine needed and used by the brain.
Hawthorn berry (Crataegus species)
This herb has traditionally been used for cardiovascular issues, including congestive heart failure, by aiding in the dilation of the coronary vessels and promoting healthy blood flow. It facilitates dilation of the blood vessels in the brain, encouraging delivery of oxygen and nutrients. Recent studies have shown promising effects on modulating anxiety in animal models.4
Hawthorn (berry) contains antioxidants and flavonoids that protect the brain from oxidative stress and support healthy inflammatory processes.
These modes of action underscore the potential of hawthorn as a natural therapeutic agent in not only cardiovascular health but also towards supporting brain health and cognitive function.
Clinical Takeaway
Canine Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome can present challenges for both dogs and their families. Fortunately, with an understanding of nutrition and implementation of nutritional supplementation, pet owners have options that may delay the onset of CCDS.
By recognizing the signs of Canine Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome (CCDS) and intervening early, pet owners can take proactive steps to provide comfort, preserve quality of life, and allow dogs to enjoy more priceless time with their families, cherishing the many benefits of the precious human-animal bond.
Read Article
Practitioner Burnout: Secrets to Supporting the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Daina Parent, ND
(0 min listen)
Episode 17 – airs February 20, 2026
In this deeply important conversation, Dr. Daina Parent, ND sits down with Dr. Jannine Krause, ND, acupuncturist, and host of The Health Fix Podcast, to explore practitioner burnout and practical strategies for restoring balance.
Dr. Jannine shares her personal journey through burnout in her own clinical practice—what led to it, how she recognized it, and the steps she took to heal and thrive again.
This episode offers actionable tools and empowering insights to help practitioners protect their energy, restore nervous system balance, and create sustainable clinical careers.
Dr. Jannine’s mission is to eliminate pain and all other limitations one may have and to inspire an active lifestyle while teaching the art of proper fueling of the body. She likes to compare herself to a private investigator. She investigates the cause of one’s complaints and comes up with a solution by removing limitations to optimal health. She uses acupuncture, prolotherapy, neural therapy, herbal medicine, nutrition and trigger point injections to eliminate pain.
She goes beyond basic nutrition and teaches the art of incorporating tonic herbs into daily meals to correct chronic conditions. Once limitations are removed one is fit to spend time doing the things they love.
Highlights of the episode include:
Exercises to tone and strengthen the parasympathetic nervous system
How nutrition and herbs influence nervous system resilience
The role of cleansing and detoxification in resetting the nervous system
Podcast Summary
1:52 – Dr. Jannine’s personal journey with practitioner burnout
5:25 – The Physician Heal Thyself course: why filling your own cup comes first
7:30 – Practical tips for establishing healthy energetic boundaries
11:45 – Simple nervous system regulation strategies for before, during, and between patient sessions
14:38 – Exercises to tone and strengthen the parasympathetic nervous system
21:21 – The significance of Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
23:06 – Epigenetic testing and biological age: connections to nervous system regulation
25:24 – Daily survival patterns and the power of thought
29:30 – How nutrition and herbs influence nervous system resilience
35:03 – Herbal support for peri- and menopause
35:20 – The role of cleansing and detoxification in resetting the nervous system
38:25 – The most important element of a foundational diet: eating close to nature
40:25 – How homegrown food impacts how we feel in our bodies
43:25 – Self-care advice for practitioners
To learn more about Dr. Jannine Krause and her work, listen to The Health Fix Podcast and visit her website at doctorkrausend.com.
This podcast is sponsored by Standard Process
About Standard Process – Only at SP
Listen to Podcast
Color of Food References
WholisticMatters
(0 min read)
The following is a list of references used the Color of Food booklet, created by the Clinical Education Team at Standard Process for WholisticMatters.
Color of Food Booklet References
Mendoza JA, Drewnowski A, Christakis DA. Dietary Energy Density Is Associated With Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome in U.S. Adults. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(4):974-979. doi:10.2337/dc06-2188
García-Blanco L, de la OV, Santiago S, Pouso A, Martínez-González M, Martín-Calvo N. High consumption of ultra-processed foods is associated with increased risk of micronutrient inadequacy in children: The SENDO project. Eur J Pediatr. Aug 2023;182(8):3537-3547. doi:10.1007/s00431-023-05026-9
Lila, M. A., & Raskin, I. (2005). Health‐related interactions of phytochemicals.Journal of food science, 70(1), R20-R27.
Lila, M. A. (2007). From beans to berries and beyond: Teamwork between plant chemicals for protection of optimal human health. Annals of the New York academy of Sciences, 1114(1), 372-380.
Nicklas, T. A., Drewnowski, A., & O’Neil, C. E. (2014). The nutrient density approach to healthy eating: challenges and opportunities. Public health nutrition, 17(12), 2626-2636.
Wang, X., Ouyang, Y., Liu, J., Zhu, M., Zhao, G., Bao, W., & Hu, F. B. (2014). Fruit and vegetable consumption and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Bmj, 349.
Monjotin, N., Amiot, M. J., Fleurentin, J., Morel, J. M., & Raynal, S. (2022). Clinical evidence of the benefits of phytonutrients in human healthcare. Nutrients, 14(9), 1712.
Rahman, M. M., Rahaman, M. S., Islam, M. R., Rahman, F., Mithi, F. M., Alqahtani, T., … & Uddin, M. S. (2021). Role of phenolic compounds in human disease: current knowledge and future prospects. Molecules, 27(1), 233.
World Health Organization (WHO, & UNICEF. (2006). Preventing and controlling micronutrient deficiencies in populations affected by an emergency. In Preventing and controlling micronutrient deficiencies in populations affected by an emergency(pp. 2-2).
National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). 2008. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data 2005-2006. Hyattsville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). 2007. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data 2003-2004. Hyattsville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. 2015. Scientific Report of the 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee: Advisory Report to the Secretary of Health and Human Services and the Secretary of Agriculture. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Washington, DC.
S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Beltsville Human Nutrition Research Center, Food Surveys Research Group (Beltsville, MD) and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics (Hyattsville, MD). What We Eat in America, NHANES 2007-2010.
Bhardwaj, R. L., Parashar, A., Parewa, H. P., & Vyas, L. (2024). An alarming decline in the nutritional quality of foods: The biggest challenge for future generations’ health. Foods, 13(6), 877.
Drewnowski, A. (2009). Defining Nutrient Density: Development and Validation of the Nutrient Rich Foods Index. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 28(4), 421S-426S. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2009.10718106
Color of Food Color Wheel References
Ma X, Jin Z, Rao Z, Zheng L. Health benefits of anthocyanins against age-related diseases. Front Nutr. 2025;12:1618072. doi:10.3389/fnut.2025.1618072
Khoo HE, Azlan A, Tang ST, Lim SM. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr Res. 2017;61(1):1361779. doi:10.1080/16546628.2017.1361779
Cappellini F, Marinelli A, Toccaceli M, Tonelli C, Petroni K. Anthocyanins: from mechanisms of regulation in plants to health benefits in foods. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2021;12:748049.
Meng X, Zhou J, Zhao CN, Gan RY, Li HB. Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms of Resveratrol: A Narrative Review. Foods. Mar 14 2020;9(3)doi:10.3390/foods9030340
Al-Khayri JM, Mascarenhas R, Harish HM, et al. Stilbenes, a Versatile Class of Natural Metabolites for Inflammation-An Overview. Molecules. Apr 28 2023;28(9)doi:10.3390/molecules28093786
Ye H, Sun J, He L, Ai C, Jin W, Abd El-Aty A. Beneficial effects of proanthocyanidins on skin aging: a review. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2025;12:1650328.
Baldelli S, Lombardo M, D’Amato A, Karav S, Tripodi G, Aiello G. Glucosinolates in Human Health: Metabolic Pathways, Bioavailability, and Potential in Chronic Disease Prevention. Foods. Mar 7 2025;14(6)doi:10.3390/foods14060912
Olayanju JB, Bozic D, Naidoo U, Sadik OA. A Comparative Review of Key Isothiocyanates and Their Health Benefits. Nutrients. Mar 7 2024;16(6)doi:10.3390/nu16060757
Harahap IA, Suliburska J. An overview of dietary isoflavones on bone health: The association between calcium bioavailability and gut microbiota modulation. Materials Today: Proceedings. 2022/01/01/ 2022;63:S368-S372. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.03.549
Musial C, Kuban-Jankowska A, Gorska-Ponikowska M. Beneficial Properties of Green Tea Catechins. Int J Mol Sci. Mar 4 2020;21(5)doi:10.3390/ijms21051744
Vezza T, Canet F, de Marañón AM, Bañuls C, Rocha M, Víctor VM. Phytosterols: Nutritional Health Players in the Management of Obesity and Its Related Disorders. Antioxidants (Basel). Dec 12 2020;9(12)doi:10.3390/antiox9121266
Lem DW, Davey PG, Gierhart DL, Rosen RB. A Systematic Review of Carotenoids in the Management of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Antioxidants (Basel). Aug 5 2021;10(8)doi:10.3390/antiox10081255
Eroglu A, Al’Abri IS, Kopec RE, Crook N, Bohn T. Carotenoids and Their Health Benefits as Derived via Their Interactions with Gut Microbiota. Advances in Nutrition. 2023/03/01/ 2023;14(2):238-255. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advnut.2022.10.007
Bufka J, Vaňková L, Sýkora J, Křížková V. Exploring carotenoids: Metabolism, antioxidants, and impacts on human health. Journal of Functional Foods. 2024/07/01/ 2024;118:106284. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2024.106284
Tan Q, Chen B, Wu C, Shao T. Exploring the potential nutritional role of bioflavonoids in exercise rehabilitation: a kinematic perspective. Front Nutr. 2023;10:1221800. doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1221800
Medina-García M, Baeza-Morales A, Martínez-Peinado P, et al. Carotenoids and Their Interaction with the Immune System. Antioxidants (Basel). Sep 12 2025;14(9)doi:10.3390/antiox14091111
Guggenheim AG, Wright KM, Zwickey HL. Immune Modulation From Five Major Mushrooms: Application to Integrative Oncology. Integr Med (Encinitas). Feb 2014;13(1):32-44.
El-Saadony MT, Saad AM, Korma SA, et al. Garlic bioactive substances and their therapeutic applications for improving human health: a comprehensive review. Frontiers in immunology. 2024;15:1277074.
Sánchez-Gloria JL, Arellano-Buendía AS, Juárez-Rojas JG, et al. Cellular Mechanisms Underlying the Cardioprotective Role of Allicin on Cardiovascular Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. Aug 13 2022;23(16)doi:10.3390/ijms23169082
Rai SN, Mishra D, Singh P, Vamanu E, Singh MP. Therapeutic applications of mushrooms and their biomolecules along with a glimpse of in silico approach in neurodegenerative diseases. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2021/05/01/ 2021;137:111377. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111377
Chugh RM, Mittal P, Mp N, et al. Fungal Mushrooms: A Natural Compound With Therapeutic Applications. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:925387. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.925387
Plant Profile References
Mountain Spinach
Clifford, T., et al., The potential benefits of red beetroot supplementation in health and disease. Nutrients, 2015. 7(4): p. 2801-2822.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Collard Greens
Clifford, T., et al., The potential benefits of red beetroot supplementation in health and disease. Nutrients, 2015. 7(4): p. 2801-2822.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Royal Ancient Oats TM Flour
Clifford, T., et al., The potential benefits of red beetroot supplementation in health and disease. Nutrients, 2015. 7(4): p. 2801-2822.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Alfalfa
Bora, K.S. and A. Sharma, Phytochemical and pharmacological potential of Medicago sativa: a review. Pharm Biol, 2011. 49(2): p. 211-20.
Rafinska, K., et al., Medicago sativa as a source of secondary metabolites for agriculture and pharmaceutical industry. Phytochemistry Letters, 2017. 20: p. 520-539.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Stochmal, A., et al., Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Flavonoids. 1. Apigenin and Luteolin Glycosides from Aerial Parts. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2001. 49(2): p. 753-758.
Barley Grass
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Kim, H., H.-D. Hong, and K.-S. Shin, Structure elucidation of an immunostimulatory arabinoxylan-type polysaccharide prepared from young barley leaves (Hordeum vulgare L.). Carbohydrate polymers, 2017. 157: p. 282-293.
Byun, A.R., et al., Effects of a Dietary Supplement with Barley Sprout Extract on Blood Cholesterol Metabolism. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2015. 2015: p. 7.
Benedet, J.A., H. Umeda, and T. Shibamoto, Antioxidant activity of flavonoids isolated from young green barley leaves toward biological lipid samples. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 2007. 55(14): p. 5499-5504.
Beetroot
Clifford, T., et al., The potential benefits of red beetroot supplementation in health and disease. Nutrients, 2015. 7(4): p. 2801-2822.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Brussels Sprouts
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Buckwheat
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Kale
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Kidney Beans
Lloyd CM, Marsland BJ. Lung Homeostasis: Influence of Age, Microbes, and the Immune System. Immunity. 2017;46(4):549-61. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.005.
Ramabulana, T., Mavunda, R. D., Steenkamp, P. A., Piater, L. A., Dubery, I. A., & Madala, N. E. (2015). Secondary metabolite perturbations in Phaseolus vulgaris leaves due to gamma radiation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 97, 287-295. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.10.018
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content.
Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Red Clover
Clifford, T., et al., The potential benefits of red beetroot supplementation in health and disease. Nutrients, 2015. 7(4): p. 2801-2822.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Peavine
Jin, A., Ozga, J. A., Lopes-Lutz, D., Schieber, A., & Reinecke, D. M. (2012). Characterization of proanthocyanidins in pea (Pisum sativum L.), lentil (Lens culinaris L.), and faba bean (Vicia faba L.) seeds.
Food Research International, 46(2), 528-535. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.11.018
Neugart, S., Rohn, S., & Schreiner, M. (2015). Identification of complex, naturally occurring flavonoid glycosides in Vicia faba and Pisum sativum leaves by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn and the genotypic effect on their flavonoid profile. Food Research International, 76, 114- 121. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.02.021
Reim, V., & Rohn, S. (2015). Characterization of saponins in peas (Pisum sativum L.) by HPTLC coupled to mass spectrometry and a hemolysis assay. Food Research International, 76, 3-10. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.06.043
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content.
Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Spanish Black Radish
Janjua, S. and M. Shahid, Phytochemical analysis and in vitro antibacterial activity of root peel extract of Raphanus sativus L. var niger. Advancement in Medicinal Plant Research, 2013. 1(1): p. 1-7.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Swiss Chard
Kugler, F., F.C. Stintzing, and R. Carle, Identification of betalains from petioles of differently colored Swiss chard (Beta vulgaris L. ssp. Cicla [L.] Alef. Cv. Bright Lights) by high-performance liquid chromatography – electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2004. 52(10): p. 2975-2981.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Turnip Greens
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Parsley
Clifford, T., et al., The potential benefits of red beetroot supplementation in health and disease. Nutrients, 2015. 7(4): p. 2801-2822.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1 ** Data on file with WholisticMattersValues subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Learn More
Read Article
Detoxification Strategies for Clinical Practice
Sarah Clarke, DC, IFMCP
(47 min listen)
Episode 16 – airs January 9, 2025
Do you know the best day to start a detoxification program in January? (HINT: It’s not January 1st!) Dr. Kim Besuden, DC, CFMP shares her tips and tricks for running successful individual and group purification programs in her practice, including best days to start, what support to offer as a practitioner, and suggestions for community support opportunities. Dr. Sarah Clarke, DC, IFMCP, host of this episode, asks Dr. Besuden what clinical signs she identifies to determine if a patient needs to detox, and how to establish healthy eating habits after the progam has finished. She shares ways to establish yourself as a nutrition leader in your community and ways she supports other practitioners in growing their practices.
Dr. Kimberly Besuden began her career in Chiropractic in 1994. Her first office located in Winter Park grew quickly. After moving to rural Lake County as a ranch owner, she opened a second satellite office in Eustis in 1998. In 2011 she purchased an office building and created Bay Street Wellness, which hosts wellness minded practitioners of massage, acupuncture, skin care, and functional medicine, as well as chiropractic care.
Dr. Besuden has a long history as a competitive athlete. This background, as well as her “hunger” for nutrition, has created her transition from a Chiropractic physician to a Certified Functional Medicine Practitioner. “I became frustrated hearing patient after patient complain about taking pills to treat symptoms.” This launched her into the journey for functional approaches to create specialized programs for patients to support them back to being well and in good health.
Use the audio player above to listen now! And don’t forget to follow and like our podcast channel to stay up-to-date on upcoming episodes.
Highlights of the episode include:
Detoxification program done by staff gives optimal support for patients
Clinical signs that a patient could benefit from a detox program
Detoxing in community helps with compliance and offers a significant learning opportunity
Podcast Summary
3:00 Detoxification program done by staff gives optimal support for patients
4:18 Appropriate timing for detox program after holidays is crucial for success
5:20 Single best way to reach out to your community and guide them through the process
6:45 Community support helps patients get through a detox program, virtually and in person
9:40 Celebrate the holidays guilt free and without withholding, it’s the amount and quality to be mindful of
10:42 5-day flash detoxes throughout the year around holidays
12:38 Advice for patients that want to continue exercising during a detox program
14:43 Clinical signs that a patient could benefit from a detox program
16:33 Adopting new healthy habits after completing a detox program
17:20 The caffeine dilemma – when to take a break and how much to drink for optimal health benefits
19:20 Top 2 improvements patients report after completing a detox program
20:00 How detox programs support liver health
21:50 Detox programs for the whole family – teaching children life long healthy habits
24:00 Food, Movement, Blood Sugar Balance, and Sleep – tools for monitoring sleep, blood sugar and more to understand each person’s biomarkers
29:34 Detoxing in community helps with compliance and offers a significant learning opportunity
30:50 I made it through the detox!… what’s next?
33:40 Clinical success stories – lab markers that indicate the need for a detoxification program
39:50 Choosing your hard and meeting patients where they’re at
44:10 Benefits of using an OTC CGM to learn about blood sugar regulation
45:36 Best way to establish yourself a leader in your community on nutrition
46:26 Dr. Besudan as a resource for other practitioners
This podcast is sponsored by Standard Process
About Standard Process – Only at SP
Listen to Podcast
Digestive Remedies to Manage Hypochlorhydria
Megan Martell, MSc
(10 min read)
Root Cause of Common Digestive Complaints
Common digestive issues such as heartburn/acid reflux, bloating, gas, indigestion, and nutrient-specific deficiencies occur if digestion is somehow altered or otherwise impaired. Many believe this is related to high levels or excessive production of stomach acid, or hyperchlorhydria, and take over-the-counter antacids or prescription Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) to suppress the acid and alleviate some of these signs and symptoms.1
When this normally acidic environment is suppressed, or buffered, to a higher pH, gaseous acid bubbles are formed, creating the feeling of gas pressure, bloating, upset stomach, or the need to belch. Furthermore, if these bubbles come in contact with the esophagus, it may be experienced as acid reflux and/or heartburn. Rather than an over-production of stomach acid, these signs and symptoms are indicative of insufficient stomach acid, or hypochlorhydria.2
Hypochlorhydria: Insufficient Stomach Acid
Hypochlorhydria has been linked to chronic inflammation of the stomach, chronic stress, H. Pylori infection, gastritis, pancreatitis, obesity, gastric-bypass surgery, as well as different autoimmune diseases, alcoholism, cirrhosis, hypertension, chronic over-use of antacids or PPIs, and aging.2,3 Regardless of the etiology, the resulting effect is the same – the stomach-acid producing and secreting cells atrophy and die off.1,2
With excessive suppression of the stomach acid, the resiliency and functionality of the stomach, digestive system, and immune system are compromised. For example, when stomach acid is suppressed, the first line of defense against stealth pathogens is disrupted and the stomach becomes more susceptible to infectious bacteria like H. Pylori. This often snowballs and leads to chronic inflammation of the stomach, or gastritis, as well as stomach ulcers, SIBO, and other bacterial overgrowths.4
Additionally, studies show the stomach operates at an optimal pH range of 1.0-2.0, while hypochlorhydria would present with a resting pH of >3.0, and regular use of antacids and PPIs have demonstrated a resting stomach pH 5.0-7.0.4 Therefore, the stomach requires more acid to lower the pH into optimal operating range so to better facilitate digestion, nutrient absorption, and general immune health.4,5
Digestion of Protein
As digestion is the physical and chemical alteration of ingested food into smaller, more soluble particles, it is required to facilitate proper nutrient absorption. The stomach in particular is responsible for the digestion of protein such as eggs, meat, dairy, legumes, nuts, and seeds. When protein reaches the stomach, specific cells- called parietal cells, secrete stomach acid, or HCl, to support digestion.
With optimal levels of stomach acid, the lowered pH denatures or unfolds the complex 3D structure of protein into a single, long protein chain, allowing for easier cleavage into short protein chains called polypeptides or single protein building blocks- amino acids.1,4,6 This happens optimally at a pH around 1.8-3.5, is especially useful for the digestion of muscle tissue and other collagen containing meat components, and is rendered inert at a higher, more alkaline pH.7 Without proper acidic conditions and without proper denaturation of the proteins, the protein molecules may not be small enough to be absorbed by the intestines, which in turn may contribute to food allergies, protein deficiency, impaired protein and DNA synthesis, and micronutrient deficiencies – specifically iron, zinc, and B12, which are largely obtained from animal sources.4
Protein-Specific Digestive Enzymes
The acidic conditions are also needed to activate the protein-specific digestive enzymes such as pepsin, which is responsible for a majority of the protein cleaving action.4 Additionally, stomach acid and other gastric secretions further facilitate the solubility, and absorption, of additional micronutrients such as vitamin C, E, B6, B12, folic acid, iron, calcium, magnesium, zinc, and copper through various, often complex, mechanisms.1,8,9
As an acidic environment is necessary for the absorption of such micronutrients, the occurrence of nutrient deficiencies is highly correlated with the occurrence of hypochlorhydria and may present as poor skin/hair/nails and slow wound healing, waning of the eyes, heart, or memory, chronic fatigue, chronic inflammation, muscle cramps/spasms, tingling in limbs, high blood pressure, and a high risk of bone fracture.1,2,4,8,9 Furthermore, if food isn’t properly digested, this may lead to, or further exacerbate, lower GI and/or elimination issues.2,10
Testing for Hypochlorhydria
As the signs and symptoms of hypochlorhydria are similar to hyperchlorhydria, the best way to tell if additional stomach acid is needed is to test for it. While there are a handful of specialized tests that a Gastroenterologist can order to test pH, secretion levels, etc, there is a quick at-home test as well. Per the Cleveland Clinic:
“Drink half a glass (4 ounces) of cold water combined with a quarter teaspoon (1/4 tsp) of baking soda, on an empty stomach.”
The baking soda will combine with the resting level of stomach acid and produce carbon dioxide, or gas bubbles. The gas bubbles will induce burping, if a burp surfaces within 3-5 minutes, then the stomach is sufficiently acidic. If it takes longer than 5 minutes, stomach acid is low and likely requires reacidification support.2 More sophisticated testing would be appropriate if there are any suspected nutrient deficiencies, food allergies, or other bacterial overgrowths.
Digestive Remedies and Interventions to Aid in Stomach Reacidification
Additionally, if stomach acid is determined to be low, there are simple interventions that would help support stomach reacidification and digestion, these include:
Sucking on or eating something sour before meals
Eating protein components of the meal first
Again, the arrival of protein in the stomach naturally triggers the secretion of stomach acid
Chewing thoroughly
This creates more surface area and further supports protein unfoldment
Eating fermented foods
That support a comprehensive and healthy microbial environment
Drinking fluids later in the meal
This allows time for the acid to work without being buffered or diluted
Acid replacement therapy or supplementation with betaine HCl
Supplementation with Betaine HCl
Studies have shown betaine HCl to have a relatively immediate effect on stomach reacidification, within 10 minutes of ingestion. The effect has been demonstrated to last around 75 minutes, which provides ample time for specific micronutrients and pH-dependent drugs to become more soluble for absorption.5 Additionally, studies have also shown that the body’s natural response to certain physiological cues decrease with age, so the elderly population may benefit from taking betaine HCl before a meal to preemptively acidify the stomach where the body’s natural response system may be slow to action and limit digestion.4
Pepsin Supplementation
To further facilitate the digestion of protein, additional supplementation of the stomach-specific enzyme pepsin, which is activated by acidic conditions, may also be warranted as it contributes to specific peptide cleavage, where these cleaved amino acids trigger other essential digestive activities, and further promotes nutrient absorption.2,11 In fact, the signaling activities of pepsin are thought to be more critical to digestion than its protein cleaving action as it triggers other digestive secretions, hormone signaling, and proper gastric emptying. Furthermore, pepsin itself has been shown to alleviate dyspeptic, or stomach acid, imbalances and is widely used in combination with betaine HCl to correct hypochlorhydria.11 However, a strong acidic environment and other beneficial stomach enzymes are still not enough to completely digest protein or the shorter polypeptide chains. As protein accounts for around 10% of our caloric intake and is needed for wound repair, tissue healing, growth and development, energy, and DNA synthesis, our body needs additional support to be able to absorb these protein-specific nutrients and amino acids in totality.7
Digestive Enzymes Secreted by the Pancreas
After the contents are released from the stomach into the first part of the small intestine, or the duodenum, the pancreas first secretes bicarbonate to buffer the acidified stomach contents. The pancreas then secretes additional digestive enzymes, which are only effective in a more buffered, or basic, solution. Of the digestive enzymes secreted, 80% are proteases, or enzymes such as pancreatin that will specifically assist the digestion of protein. The additional 20% of the pancreatic digestive enzymes support the digestion of the other macronutrients – carbohydrates and fat. 7,12
Pancreatin
Pancreatin, in particular, finishes the hydrolysis process by fully transforming the bulky protein molecule, or peptide chain, into single amino acids and further promotes total macronutrient absorption .7 Without this major component of enzymes, protein goes largely undigested, the other macronutrients go unabsorbed, tissue growth and repair is inhibited, and nutrient deficiencies are common.12 Therefore, additional digestive enzyme supplementation may also be supportive if signs and symptoms, such as fatigue, slow wound healing, nerve/muscle pain, frailty and/or other bone-related concerns, are present independently or in combination with other GI concerns.
Clinical Takeaways
Digestive concerns, such as acid reflux, heartburn, gas, bloating, and belching, are synonymous with dyspepsia and assessing stomach acid levels may be worthwhile to better facilitate and improve (protein) digestion, and ultimately, absorption.
If testing confirms hypochlorhydria, supplementing with betaine HCl would be beneficial to promote stomach reacidification and digestion.
Digestive remedies such as betaine HCl, further fortified with pepsin and pancreatin, would then support a highly acidic environment, appropriate and healthy digestive signaling, nutrient absorption, and immune health, while addressing and alleviating other common digestive symptoms, malabsorption, and nutrient deficiencies.
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Learn More
Read Article
Consuming Organ Meats: Nutritional and Traditional Significance
Sarah Clarke, DC, IFMCP
(39 min listen)
Episode 15 – airs December 4, 2025
Dr. Sarah Clarke, DC, IFMCP, and Dave Hogsed, DOM, AP, discuss traditional and cultural trends around the consumption of organ meats, and the nutritional value these foods offer. They cover nutrients found various organ meats and how they can either be eaten or taken in supplement form. Dave shares clinical success stories, including his own personal experience, using organ meat glandular therapy. He explains how various organ and glandular meats can support immune function, cardiovascular health, nervous system health, cognitive function, bone health, and more.
David Hogsed, DOM, AP, is in full time practice at the Natural Healthcare Professionals clinic in Fort Myers, Florida. His practice specializes in providing effective nutritional support for endocrine, digestion, musculoskeletal, nervous system, and immune system health. David has been a clinical consultant and speaker for Standard Process since 2003. His seminars are best known for simplifying clinical nutrition, herbal medicine, laboratory tests, and patient education.
David has taught post-graduate programs through Texas Chiropractic College, Logan Chiropractic College, the University of Miami-Miller School of Medicine, Palmer Chiropractic College, Life University, and Northwestern Chiropractic College. He is a regular speaker for the Florida Chiropractic Association, and Palmer Chiropractic College homecoming.
Use the audio player above to listen now! And don’t forget to follow and like our podcast channel to stay up-to-date on upcoming episodes.
Highlights of the episode include:
Organ Meats: the forgotten superfoods – historical consumption around the world
Liver: the most nutrient dense organ meat
Studies and historical evidence of health benefits of organ meats
Podcast Summary
2:40 Dave’s first personal success story with organ meat glandular therapy
5:15 Clinical results from combining organ meat supplements with herbal and nutritional support
7:06 Organ Meats: the forgotten superfoods – historical consumption around the world
8:50 Traditional Chinese Medicine – consumption of organ would support that organ
9:48 Liver: the most nutrient dense organ meat
12:04 Returning popularity of other traditional foods – raw sauerkraut, bone broths, cod liver oil, and more
12:46 Foods essential for health – “you must take it (as a supplement) or eat it”
14:00 Tips for incorporating liver into your diet
15:03 Key benefits of bone broth and bone extracts
16:53 Animals instinctively know the health benefits of organ meats
18:06 The consumption of heart for cardiovascular health
21:30 Combating the effects of stress with organ meats: liver and adrenal glandular extract
23:30 Studies are now finding additional nutritional benefits in organ meats – mRNA
24:21 Nutritional difference between skeletal muscle meat vs. organ meat
27:24 Studies and historical evidence of health benefits of organ meats
28:17 Liver: the ultimate multivitamin
31:00 Organ meats for immune support – thymus extract
32:40 Historical consumption of brain around the world for cognitive health
34:49 Testicular and ovarian extracts for hormone regulation
35:40 The importance of thymus extracts in young children and with aging populations
36:46 Liver is the king of organ meats
This podcast is sponsored by Standard Process
About Standard Process – Only at SP
https://youtu.be/xvFpIr2ctgE?si=mx-9S1UGDD8IKIDw
Listen to Podcast
The Effects of Stress on a Woman’s Body: Female Hormones and Endocrine Health
Daina Parent, ND
(67 min listen)
Episode 14 – airs November 20, 2025
Why is it that women experience stress more intensely than men? Drs. Daina Parent and Annette Schippel discuss the connection between women’s hormones and the effects of stress on the female body. Dr. Schippel shares her personal and professional experience navigating the stages of a woman’s reproductive journey and how endocrine health plays a significant role in hormone balance. Drs. Parent and Schipple emphasize the importance of working with qualified healthcare providers trained in herbal medicine in order to find the right herbs for each person and symptom picture. Dr. Schippel offers invaluable clinical tools and takeaways to create a strong foundation for any woman to navigate stress management and optimal wellness with nutrition, herbs, lifestyle and more.
Dr. Annette Schippel is a chiropractor and a graduate of Logan College of Chiropractic, she brings over 25 years of experience to her work. She owns two thriving family practices that focus on pediatrics, women’s health, and clinical nutrition, and she regularly sees patients from across the United States and around the world.
Known for her expertise in functional medicine and endocrinology, Dr. Schippel has become a respected educator, author, and speaker. She has written and co-authored numerous clinician manuals and lectures domestically and internationally on topics in nutrition and functional endocrinology. She has had the privilege of visiting Medi-Herb in Australia for 3 years to receive advanced training in phytotherapy. She also had the honor to speak on alternative approaches to Metabolic Syndrome at the 2014 International Health Management Forum in Bejing China.
Use the audio player above to listen now! And don’t forget to follow and like our podcast channel to stay up-to-date on upcoming episodes.
Highlights of the episode include:
Female hormones and stress sensitivity
Adrenal burnout and perimenopause: the resiliency of the stress response affects hormone balance
How herbs modulate and synergize with hormones
Podcast Summary
2:24 Female hormones and stress sensitivity
4:00 The HPA Axis and the stress response
5:35 The thyroid adrenal connection
7:57 Cortisol, DHEA and the adrenal cortex
9:15 Prolactin, dopamine and high prevalence of autoimmunity in women
11:30 Key differences in male and female hormones: estradiol, testosterone, and DHEA
15:27 Peri- and menopausal hormone shifts
16:33 Adrenal burnout and perimenopause: the resiliency of the stress response affects hormone balance
21:13 Clinical strategies for adrenal support to mitigate perimenopausal symptoms – diet, exercise, sleep, digestion, and mental health
25:42 Herbs for adrenal support and endocrine balance – rehmania, ashwagandha, chaste tree, schizandra and more
29:33 How herbs modulate and synergize with hormones
30:02 Social media trends – perspectives on ashwagandha
33:06 Why guidance from a healthcare provider with herbal knowledge matters – finding the right herbs for each person
35:35 Choosing the right herb – how patient health history and symptom picture inform herbal selection
44:39 Using blood chemistry to inform patient protocols
45:55 Personalizing herbal protocols for different stages of the lifespan
48:38 Nutrients and herbs for libido and vaginal dryness and how adrenal resilience plays a role in these symptoms
50:32 Circulation, sexual health, and blood-flow support
52:53 Improving vasodilation through nitric oxide; whole foods and herbs that support circulation (beets, mountain spinach, red algae, and more)
54:45 Herbs as modulators – herbs won’t increase or decrease hormones too much
55:16 The truth about wild yam creams
58:54 The practitioner-patient journey – navigating better health together
1:01:51 Key clinical takeaway for supporting women’s health and stress management – how to build a good foundation and never lose sight of what you’re trying to build
This podcast is sponsored by Standard Process
About Standard Process – Only at SP
https://youtu.be/06W6QnbDbSU?si=HhkXX9NerHPbhcDu
Listen to Podcast
The Role of Adaptogens and Nervines in Stress Recovery
Aneeta Uppal, PhD, MS, IHP
(0 min read)
Physiology Meets Phytotherapy
Any stressful situation, whether it is a family emergency, the deadline for a project, fear about losing a job, worry about not paying the bills on time, can trigger a cascade of signals in the body that release specific hormones that cause physiological changes in the body. This is known as the “fight” or “flight” response. These changes can manifest as a rapid heartbeat, sweat, tense muscles, headache, digestive problems, elevated body temperature, and more. Stress is the response to a real or perceived threat that disrupts the body’s homeostasis. The acute stress response is essential for survival, however, when the acute stress response is not shut off, there can be significant long-term health ramifications. As this acute response becomes prolonged, stress shifts from an adaptive reaction to a chronic condition.
Chronic Stress and the HPA Axis
Chronic stress occurs when there is prolonged exposure to stressful situations. This can be caused by long-term issues such as health problems, relationship issues, and problems at work. Overstimulation from technology and smart phones also contributes significantly to the overall increase in the experience of stress.
Anxiety disorders have seen an 18.2% increase from 1990 to 2021 globally.1 Following Covid, over half of the population experienced emotional stress in 20 countries, and 85% of the countries reported worse psychological stress in 2020 compared with 2008.2 Chronic stress over time can wreak havoc in the body on your neurological health, hormone balance, and physical and mental health. Over time, this chronic stress can lead to Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis dysfunction.
The HPA axis consists of:
Hypothalamus – the part of the brain responsible for regulating temperature, hunger mood, and more. It influences the autonomic nervous system and manages hormones.
Pituitary gland – small gland located on the base of the brain below the hypothalamus. It makes essential hormones needed for the body and regulates other endocrine glands.
Adrenal glands – small triangular shaped glands on the top of each kidney. They produce hormones like cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens that regulate blood pressure, stress response, metabolism, immune system, and sexual health. The adrenal glands also produce Epinephrine (the hormone that prepares the body for the flight or fight response) and norepinephrine.
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenals that is crucial to survival. It helps the body respond to stress, regulate blood sugar, metabolism, hormone regulation, and maintain blood pressure. The body is constantly producing, in varying concentrations throughout a 24-hour cycle. Typically, it is produced in higher amounts or stays elevated in those with a heightened fight/flight response.
When cortisol levels rise significantly, it signals the hypothalamus to reduce the release of corticotrophin releasing hormone (CRH), which then leads to decreased ACTH production by the pituitary gland. High cortisol can inhibit and decrease production of other hormones like estrogen and progesterone which can lead to menstrual irregularities.
Naturally cortisol levels should fluctuate throughout the day, being higher in the mornings and lower in the evenings. In the evenings, the body will produce melatonin and decrease cortisol production to facilitate a more restful state. In cases of chronic stress, cortisol can stay elevated for longer periods of time, and its patterns become more irregular.
Herbal Remedies for Chronic Stress
Given these physiological consequences, addressing chronic stress requires interventions that support both the nervous system and endocrine system. Herbal medicine can provide tremendous relief for those that experience acute or chronic stress. Numerous herbs have been utilized traditionally and effectively for managing both stress and anxiety. Herbs can be broken down into multiple therapeutic areas.
Adaptogens
Adaptogens, a term coined in the 1940’s, improve the body’s non-specific resistance to stress.3 Adaptogens accomplish this through their abilities to reduce oxidative stress, protect the mitochondria, normalize cortisol levels, and by regulating the HPA axis. Several adaptogens, including astragalus (Astragalus membranaceous), ashwagandha (Withania somniferum), licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra), and rhodiola (Rhodiola rosea), have a long history of use in traditional herbal medicine for improving resilience to chronic stress, and have been shown in modern research to address multiple aspects of the stress response and more.
Nervines
Nervines are a category of plants that help to support the nervous system by relieving stress and helping to promote relaxation.4 Nervines, including lavender (Lavandula), skullcap (Scutellaria lateriflora), passionflower (Passiflora) and valerian (Valeriana officinalis) are plants that help to support the nervous system by relieving stress and promoting relaxation. Nervines are commonly used in conjunction with adaptogens due to the overlapping benefits. These work by acting on the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system to help improve overall resilience to stress.5 Nervines are categorized by nervine tonics, nervine relaxants, and nervine stimulants. Nervines typically have a fast-acting effect on the nervous system, making them more appropriate for addressing acute stress, while adaptogens work at a deeper level to support nervous system homeostasis.
Nervine Spotlight on Skullcap
Within these categories, several herbs stand out for their synergistic potential. Skullcap (Scutellaria Lateriflora), commonly known as “blue skullcap” and “American skullcap” is hardy perennial herb that belongs to the mint family (Lamiaceae), and is native to North America. Its traditional uses dates to the Indigenous people of North America who traditionally consumed it as a tea to help soothe nerves, as a sedative, and anticonvulsant.6 Today in western herbal medicine, skullcap is utilized to help relieve nervous tension, anxiety, combat insomnia, neuralgia, and epilepsy.7
Skullcap aerial parts consist of phytochemicals like flavonoids, glycosides, cinnamic acid and caffeic acid.6 Skullcap acts as a nervine tonic, spasmolytic and in higher doses, a sedative. It can have restorative effects on the nerves, physically and mentally/emotionally. One study summarized key findings of a significant sleep-wake balance improvement when supplemented with Skullcap in a controlled, randomized, crossover double blind clinical trial.8
Adaptogenic Actions of Licorice
Transitioning from nervines to adaptogens, licorice root is an adaptogen that has historically been used forbronchitis, throat infections, liver diseases, gastritis, peptic ulcerations, and adrenal insufficiency.7,9 It has a long history of use in traditional Asia and European herbal medicine and has since been commercially grown all over the world due to its multitude of uses in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.10
Transitioning from nervines to adaptogens, licorice root is an adaptogen that has historically been used forbronchitis, throat infections, liver diseases, gastritis, peptic ulcerations, and adrenal insufficiency.7,9 It has a long history of use in traditional Asia and European herbal medicine and has since been commercially grown all over the world due to its multitude of uses in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.10
Licorice’s main medicinal properties act as an anti-inflammatory, expectorant, demulcent, anti-microbial, and adrenal tonic. Licorice’s main key constituents consist of: saponins, glycyrrhizin (glycyrrhizic acid) present in the form of potassium and calcium salts and flavonoids.7 In animal models, licorice root was studied and noted to reduce anxiety and fear in post-traumatic stress disorder subjects.11 Glycyrrhizin from licorice root has been shown to contain antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune regulatory actions.12
Adaptogen Spotlight on Ashwagandha
Another cornerstone adaptogen, ashwagandha, has a long historical use as an adaptogen to strengthen the nervous system and combat stress. Ashwagandha holds therapeutic properties as a mild sedative, anti-inflammatory, immune modulating, neuroprotective, and anti-microbial.13 Its medicinal uses trace back to Indian medicine over 3,000 years ago.14 Traditionally, it has been used as an aphrodisiac, narcotic, tonic, diuretic, anthelmintic, and stimulant. It is naturally native in India but due to its current widespread popularity, it is now grown in many parts of the world.15
Another cornerstone adaptogen, ashwagandha, has a long historical use as an adaptogen to strengthen the nervous system and combat stress. Ashwagandha holds therapeutic properties as a mild sedative, anti-inflammatory, immune modulating, neuroprotective, and anti-microbial.13 Its medicinal uses trace back to Indian medicine over 3,000 years ago.14 Traditionally, it has been used as an aphrodisiac, narcotic, tonic, diuretic, anthelmintic, and stimulant. It is naturally native in India but due to its current widespread popularity, it is now grown in many parts of the world.15
Ashwagandha contains withanolides, alkaloids, and flavonoids.13 A recent study displayed that ashwagandha root extract may help improve sleep quality and sleep onset latency in patients with insomnia.16 Multiple studies have found that standardized ashwagandha root extracts reduce perceived stress, anxiety and lower cortisol when compared to placebos.16-18 Recent trials have shown improvements in endurance, strength and recovery in healthy adults and athletes using specific ashwagandha extract formulations. 19
Korean Ginseng as Adaptogen and Tonic Herb
Korean ginseng has been traditionally used for athletic and psychomotor performances, depression, and sexual function.7 Its main actions include: adaptogenic, tonic, immune modulating, cardiotonic, male tonic, cancer preventative, and cognition enhancing.7 The key constituents of ginseng include a complex mixture of saponins, ginsenosides, oleanolic saponin, polysaccharides, and essential oils.
Korean ginseng has been traditionally used for athletic and psychomotor performances, depression, and sexual function.7 Its main actions include: adaptogenic, tonic, immune modulating, cardiotonic, male tonic, cancer preventative, and cognition enhancing.7 The key constituents of ginseng include a complex mixture of saponins, ginsenosides, oleanolic saponin, polysaccharides, and essential oils.
Ginsenosides, the main phytochemical of ginseng, has been studied for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in cell and animal models by modulating NF-kB and JAK/STAT pathways.20 Several small, randomized controlled trials found modest improvements in attention and working memory.21 Additional studies have been conducted to study ginseng and its role in fatigue, physical performance, and its cardiometabolic effects.22,23
Clinical Takeaways
Chronic stress represents one of the most pervasive disruptors of physiological balance, influencing the HPA axis, hormone regulation, and overall neurological resilience. A combination of nervines and adaptogens offers a powerful therapeutic strategy. Nervines such as skullcap provide rapid relief of nervous tension, calming the hyperactive sympathetic response and promoting relaxation, while adaptogens like Ashwagandha, licorice root, and Korean ginseng, work more deeply to restore HPA axis function, regulate cortisol, and build long-term resilience to stress.
In a clinical setting, this synergistic partnership allows for both immediate soothing of the nervous system and gradual rebalancing of hormonal and metabolic function. Together, these herbs bridge acute symptom relief with long-term adaptation, offering a holistic, evidence-informed approach to managing modern stress in all its physiological and psychological challenges.
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Learn More
Read Article
Turnip Greens: Whole Food Profile
WholisticMatters
(5 min read)
Turnip greens come from the leaves of root vegetable Brassica rapa subsp. rapa and are a particularly rich source of vitamins K, E, and B6 as well as plant form folate and phytoactive compound lutein. The dry leaves from turnips are also a rich source of glucosinolates and the activating enzyme myrosinase.
Key Nutrients in Turnip Greens
Percentages shown as %DV per serving of 5.68g turnip greens.
Total Phenolic Concentration in Turnip Greens
Measured: Total Phenolics as Gallic Acid Equivalence (mg/g).
Phytoactives in Turnip Greens
Glucosinolates
Sulfur-containing secondary metabolites mostly found in cruciferous vegetables, when activated by myrosinase from the plant or after ingestion by gut bacteria, associated with positive effects stemming from antioxidant activity such as cardio-protection and detoxification support
Other Glucosinolates (4.12 mg/g)** Neoglucobrassicin (1.74mg/g)**
Glucoraphasatin (1.2 mg/g)** Glucobrassicanapin (1.06 mg/g)**
Flavonols
Promote antioxidant activity and vascular health
Kaempferol (31.7 mcg/g)*
Quercetin (4.9 mcg/g)*
Phenolic Acids
Phytoactive compounds that promote anti-oxidant activity and vascular health
Caffeic Acid(29.5 mcg/g)*
Gallic Acid (23.1 mcg/g)*
Ferulic Acid (6.0 mcg/g)*
Protocatechuic Acid (6.0 mcg/g)*
Myrosinase
Enzyme found in plant tissue that initiates conversion of glucosinolates to bioactive isothiocyanates
Ellagic Acid
Potential antioxidant compound with anti-cancer potential
Chloryphyll
Green pigment in plants with potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-bacterial activity
Carotenoids
Antioxidants with anti-cancer potential and may lower risk of macular degeneration
Beta-carotene(220.8 mcg/g)**
*Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1
**Data on file with WholisticMatters. Values subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Learn More
Download PDF
Read Article
Swiss Chard: Whole Food Profile
WholisticMatters
(5 min read)
Dark leafy greens with vibrantly colored stems and veins are trademark features of Swiss chard (Beta vulgaris subsp. cicla). This plant is a mineraldelivery powerhouse.
Key Nutrients in Swiss Chard
Percentages shown as %DV per serving of 5g dry Swiss chard extract.
Total Phenolic Concentration in Swiss Chard
Measured: Total Phenolics as Gallic Acid Equivalence (mg/g).
Phytoactives in Swiss Chard
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants with potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-bacterial activity
Flavonols
Promote antioxidant activity and vascular health
Kaempferol(92 mcg/g)*
Quercetin(75 mcg/g)*
Myricetin(22 mcg/g)*
Lignans
Cross-linked phenolic compounds that make up plant cell walls and are insoluble fibers that aid in fecal bulking and feed some gut bacteria
Secoisolariciresinol (0.07 mcg/g)*
Betalains
Natural pigments with antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-lipidemic, and antimicrobial properties
Betacyanins
Betaxanthins
Carotenoids
Antioxidants with anti-cancer potential and may lower risk of macular degeneration
Lutein (1.45 mg/g)**
Zeaxanthin(10.6 mg/g)**
Beta-carotene (52.26 mg/g)**
*Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1
**Data on file with WholisticMatters. Values subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Learn More
Download PDF
Read Article

Explore Our Complimentary Continuing Education
Expand your expertise and support your professional status with our CE-accredited courses. We recognize the importance of staying up to date with your credential requirements and the latest in research and clinical care techniques.
Herbal Glossary
Find detailed information on various herbs, their benefits, and how to effectively incorporate them into patient care.