Part 8 Immune System Series | Strategies to Support Gut Health
Summary
Gut health is essential for optimal immune system functioning. Lifestyle and environmental factors such as diet, hygiene, and exercise impact the composition of the microorganisms that colonize our human body, collectively referred to as the microbiome.
Compositional and functional alterations of the of the gut microbiome have been associated with a host of multifactorial diseases including inflammatory, autoimmune, metabolic, neoplastic, and neurodegenerative disease.1-2 Lifestyle and environmental factors such as diet, hygiene, and physical activity impact the composition of the microorganisms that colonize our human body, collectively referred to as the microbiome.
What is the Microbiome?
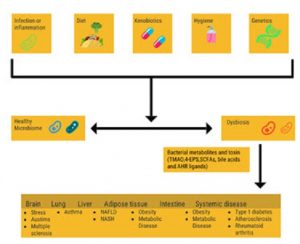
Intestinal dysbiosis refers to the taxonomical composition as well as function of the microbial community. The microbiome in this context includes bacterial, fungal, viral, and protozoan communities that exist in communities on and in our human bodies. The human gastrointestinal (GI) tract is host to over 100 trillion bacteria, including more than 500 species that account for 10-times as many cells as there are human cells in the body.3-4
A highly diverse microbiome ecosystem is a factor that supports stability, resistance, and resilience of the microbial community, that contributes to health and reduce the incidence of microbial pathogens. The imbalance between mucosal barriers and gut microbes promotes susceptibility to intestinal inflammation.5 A healthy and diverse microbiome supports gut health; and an unhealthy microbiome (dysbiosis) can lead to digestive disorders. Digestive health disorders affect between 60-70 million Americans annually and account for over 48 million ambulatory care visits, 21.7 million hospitalizations, and, in 2009, an estimated 246,000 deaths per year in the United States.6
There is extensive inter-individual variability in the composition of the microbiome of healthy individuals as demonstrated by the Human Microbiome Project.7 However, in the condition of dysbiosis, in which the microbiome contributes to digestive health disorders, there is a blend of non-mutually exclusive characteristics.1 Different types of dysbiosis that have been characterized that contribute to digestive health disorders include:
- Pathobionts: Pathiobionts are resident bacteria (commensal microbiota) that can cause pathology (but are typically present at low relative abundance). They “bloom”, resulting in an increase in the relative abundance of the bacterial species with adverse consequences to the intestinal ecosystem. An example of a pathiobiont is commensal bacteria Enterobacteriaceae, which is frequently observed in enteric infection and inflammation such as in patients with IBD, with a concomitant depletion of the phyla Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes.8 It is not known whether the growth of pathobionts is a consequence or a cause of the inflammation-induced remodeling of the intestinal ecosystem.
- Loss of Commensals: As the outgrowth of pathobionts blooms, the relative abundance of commensal bacteria (resident bacteria that neither affect nor benefit from their human host, such as Escherichia coli) is reduced. In a pre-clinical setting of inflammation, replenishment of commensal bacteria colonization with Clostridium scindens reduced inflammation, caused by an increase in pathogenic Clostridium difficile.9 Additional research will add options for microbiome reconstitution approaches that can be used to treat dysbiosis-associated phenotypes of inflammation.
- Loss of Diversity: A decrease in microbiome diversity predisposes patients to dysmetabolism and low grade inflammation.10-11 Microbiome diversity is increased from birth to old age, and is a key contributor to a healthy gastrointestinal tract.12
Strategies to Support Gut Health
Strategies to enhance intestinal health should target support of the microbiota of the gastrointestinal tract along with enhanced diet, hygiene, and regular exercise. Many clinicians recommend the use of targeted probiotics (genus, species, and strains of bacteria) to promote enhancement of the microbiota, particularly after a round of antibiotics. Another approach, and one that can be used in combination with others, is to ingest a diet rich in prebiotics, which are components of food (fiber) that are non-digestible by the typical enzymatic capacity of the human, but can be digested (fermented) by the colonic bacteria.
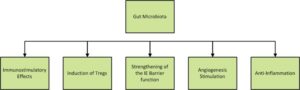
The intestinal microbiota residing in the lumen ferment undigested fibers and produce short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate and propionate, which can be absorbed by the intestinal epithelial cells.13-14 Once absorbed, the SCFA migrate to the lamina propria and signal the stimulation of dendritic cells of the innate immune system to synthesize cytokine IL-10, which then stimulates the further production of IL-10 by regulatory T cells of the acquired immune system. This metabolite-innate immunity crosstalk originates before birth and is part of the intricate and complex network of innate and acquired immunity providing protection from environmental pathogens. The role of the commensal gut microbiota on immunostimulatory effects, induction of regulatory T cells, strengthening of the intestinal epithelial barrier function, angiogenesis stimulation, and anti-inflammation is reviewed by Lin et al., and is illustrated in the Figure.2
Read part 9 of the Immune System Series: The Role of Aging, Exercise, and Diet in Immune Function.
- Levy, M., Kolodziejczyk, A.A., et al. (2017). Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 17(4): 219-232.
- Lin, L., Zhang, J. (2017). Role of intestinal microbiota and metabolites on gut homeostasis and human disease. BMC immunology 18(1): 1-25.
- Turnbaugh, P. J., Ley, R.E., et al. (2007). The human microbiome project. Nature 449(7164): 804-810.
- Wilson, M. (2005). An introduction to the human-microbe symbiosis. Microbial Inhabitants of Humans: Their Ecology and Role in Health and Disease. New York, Cambridge University Press: 1-50.
- Okumura, R., Takeda, K. (2017). Roles of intestinal epithelial cells in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Exp Mol Med 49: e338.
- (November 2014, May 8, 2017). Digestive disease statistics for the United States. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/digestive-diseases.
- Consortium, H. M. P. (2012). Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 486(7402): 207-214.
- Frank, D. N., St Amand, A.L., et al. (2007). Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104(34): 13780-13785.
- Buffie, C. G., Bucci, V., et al. (2015). Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile. Nature 517(7533): 205-208.
- Cotillard, A., Kennedy, S.P., et al. (2013). Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature 500(7464): 585-588.
- Le Chatelier, E., Nielsen, T., et al. (2013). Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 500(7464): 541-546.
- Yatsunenko, T., Rey, F.E., et al. (2012). Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 486(7402): 222-227.
- Sabater-Molina, M., Larque, E., et al. (2009). Dietary fructooligosaccharides and potential benefits on health. Journal of physiology and biochemistry 65(3): 315-328.
- Frei, R., Akdis, M., et al. (2015). Prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics, and the immune system: experimental data and clinical evidence. Current opinion in gastroenterology 31(2): 153-158.