Two Forms of EPA & DHA Delivery
About this PDF
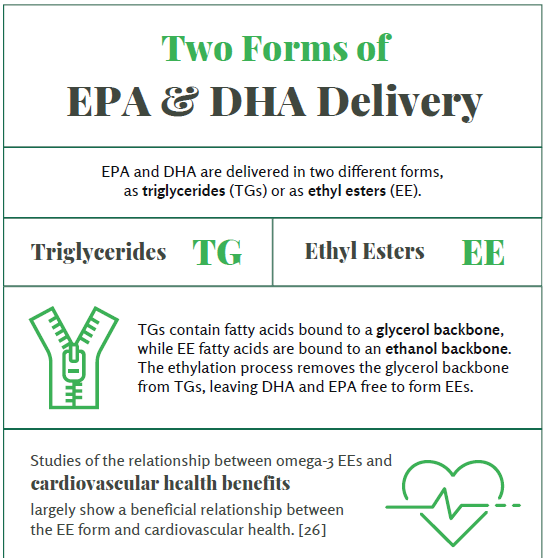
Omega-3 fatty acids are an important part of the diet, but not every fatty acid is created equally. They can be delivered in two different forms, each with unique properties. Triglycerides (TGs) deliver fatty acids that are bound to a glycerol backbone, while ethyl esters (EEs) deliver fatty acids bound to an ethanol backbone. TG is the natural form, and through a process called ethylation, the omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA are cleaved from the glycerol backbone, allowing them to form EEs. The ethyl ester form is commonly used for condition-specific interventions, and studies have found a beneficial relationship between omega-3 fatty acids in EE form and cardiovascular health.