Turnip Greens: Whole Food Profile
Turnip greens come from the leaves of root vegetable Brassica rapa subsp. rapa and are a particularly rich source of vitamins K, E, and B6 as well as plant form folate and phytoactive compound lutein. The dry leaves from turnips are also a rich source of glucosinolates and the activating enzyme myrosinase.
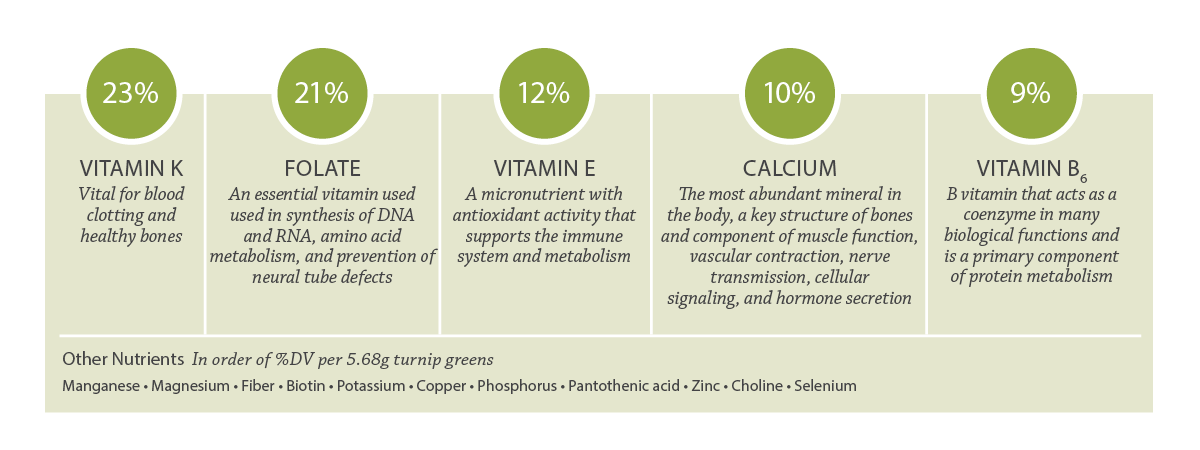
Key Nutrients in Turnip Greens
Percentages shown as %DV per serving of 5.68g turnip greens.
Phytoactives in Turnip Greens
Glucosinolates
Sulfur-containing secondary metabolites mostly found in cruciferous vegetables, when activated by myrosinase from the plant or after ingestion by gut bacteria, associated with positive effects stemming from antioxidant activity such as cardio-protection and detoxification support
- Other Glucosinolates (4.12 mg/g)** Neoglucobrassicin (1.74mg/g)**
- Glucoraphasatin (1.2 mg/g)** Glucobrassicanapin (1.06 mg/g)**
Flavonols
Promote antioxidant activity and vascular health
- Kaempferol (31.7 mcg/g)*
- Quercetin (4.9 mcg/g)*
Phenolic Acids
Phytoactive compounds that promote anti-oxidant activity and vascular health
- Caffeic Acid(29.5 mcg/g)*
- Gallic Acid (23.1 mcg/g)*
- Ferulic Acid (6.0 mcg/g)*
- Protocatechuic Acid (6.0 mcg/g)*
Myrosinase
Enzyme found in plant tissue that initiates conversion of glucosinolates to bioactive isothiocyanates
Ellagic Acid
Potential antioxidant compound with anti-cancer potential
Chloryphyll
Green pigment in plants with potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-bacterial activity
Carotenoids
Antioxidants with anti-cancer potential and may lower risk of macular degeneration
- Beta-carotene(220.8 mcg/g)**
*Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1
**Data on file with WholisticMatters. Values subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.

