Spanish Black Radish: Whole Food Profile
Spanish Black Radish (Raphinoussativus L. Var. niger) is a cruciferous vegetable associated with the production of detoxification enzymes, healthy digestion, and healthy liver and gallbladder function. Spanish black radish is grown for its rich supply of glucosinolates.
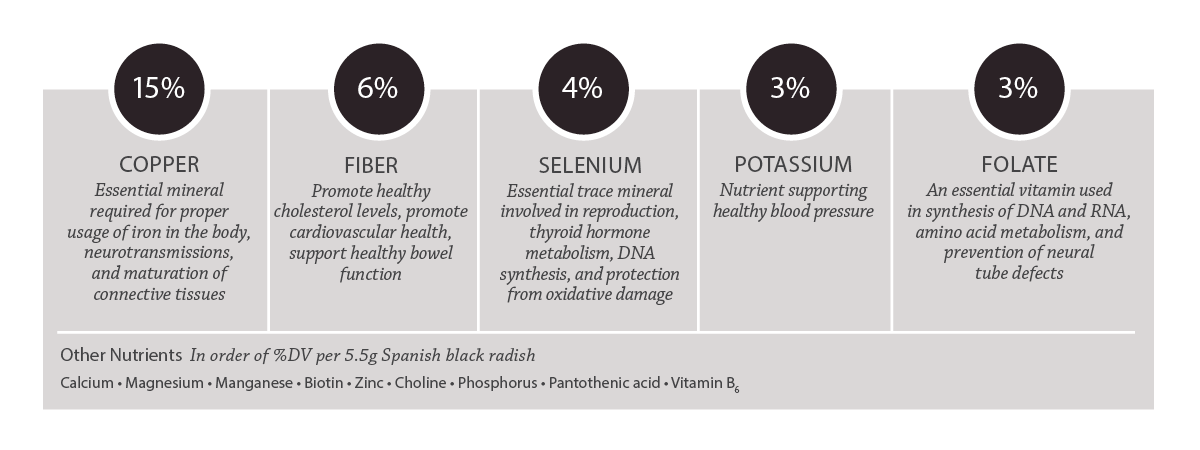
Key Nutrients in Spanish Black Radish
Percentages shown as %DV per serving of 5.5g Spanish black radish.
Total Phenolic Concentration in Spanish Black Radish
Measured: Total Phenolics as Gallic Acid Equivalence (mg/g).

Phytoactives in Spanish Black Radish
Glucosinolates
Sulfur-containing secondary metabolites mostly found in cruciferous vegetables, when activated by myrosinase from the plant or after ingestion by gut bacteria, associated with positive effects stemming from antioxidant activity such as cardio-protection and detoxification support
- Glucobrassicin (11.835 mg/g)**
- Sinigrin (0.215 mg/g)**
- Gluconapin (0.2 mg/g)**Glucoraphanin (0.12 mg/g)**
- Glucoerucin (0.095 mg/g)**
- Glucobrassicin (0.082 mg/g)**
- Glucobrassicanapin (0.058 mg/g)**Glucoraphenin (0.004 mg/g)**
- Neoglucobrassicin (0.002 mg/g)**4-MeOH Glucobrassicin (0.002 mg/g)**
Saponins
Compounds that support the immune system, healthy cholesterol levels, and blood glucose levels
Tanins
Large set of diverse phenolic compounds found in plants that contribute to antioxidant activity, antimicrobial action, and distinct dark color
Myrosinase
Enzyme found in plant tissue that initiates conversion of glucosinolates to bioactive isothiocyanates
Fiber
Supports cardiovascular health, healthy bowel function, and healthy cholesterol levels
*Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1
**Data on file with WholisticMatters. Values subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Janjua, S. and M. Shahid, Phytochemical analysis and in vitro antibacterial activity of root peel extract of Raphanus sativus L. var niger. Advancement in Medicinal Plant Research, 2013. 1(1): p. 1-7.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.

