Kidney Bean: Whole Food Profile
The material of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) is rich with iron, magnesium, folate, fiber, and thiamin, among other macro- and micronutrients. The sprouts and full-grown plant contain ample amounts of essential minerals, various vitamins, and phenolic compounds.
Key Nutrients in Kidney Bean
Percentages shown as %DV per serving of 5g kidney bean juice extract.

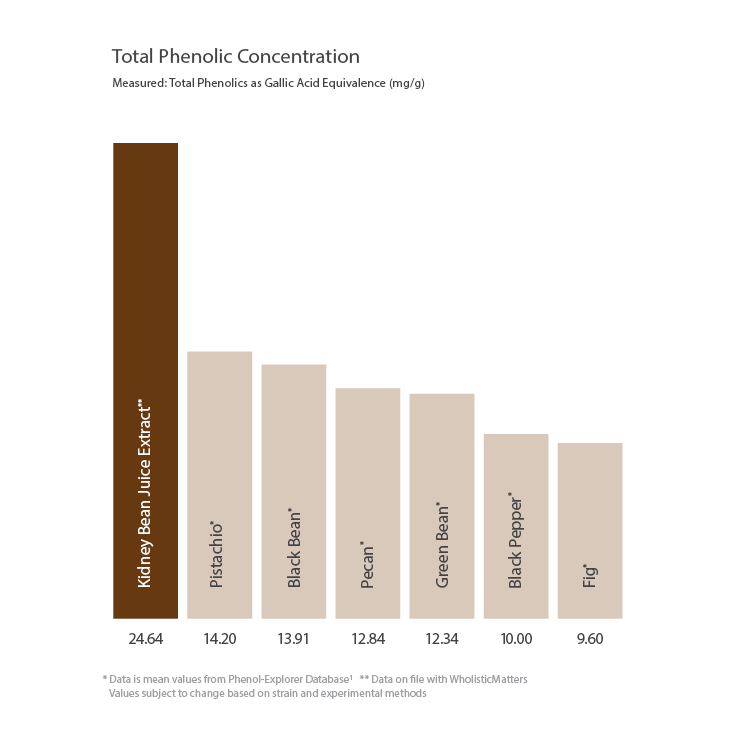
Total Phenolic Concentration in Kidney bean
Measured: Total Phenolics as Gallic Acid Equivalence (mg/g).
Phytoactives in Kidney Bean
Saponins
Support the immune system, healthy cholesterol levels, and blood glucose levels
- Bayogenin
- Soyasaponin I
- Soyasaponin V
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants with potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-bacterial activity
Lignans
Large plant polyphenolic compounds that bypass human digestion, feed gut bacteria, and provide antioxidant activity
- Lariciresinol (1.2 mcg/g)* Secoisolariciresinol (0.8 mcg/g)*
- Pinoresinol (0.3 mcg/g)* Syringaresinol (0.08 mcg/g)*
Phenolic Acids
Compounds that promote antioxidant activity and vascular health
- Ferulic Acid (128.4 mcg/g)* Sinapic Acid (51.7 mcg/g)*
- p-Coumaric Acid (38.1 mcg/g)* Coumaroyl-malate
- Feruroyl-malate
Isoflavonoids
Phenolic compounds with direct antioxidant effects
- Genistein (2.0 mcg/g)*
Flavonols
Promote antioxidant activity and vascular health
- Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside (398.8 mcg/g)*
- Quercetin-3-glucoronide2(286 mcg/g)*
- Kaempferol-3-O-acetyl-glucoside (164 mcg/g)*
- Kaempferol-3-O-xylosyl-glucoside (115 mcg/g)*
- Kaempferol (12.2 mcg/g)*Quercetin (6.8 mcg/g)* Kaempferol-3-glycoside
- Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside Quercetin-3-acetyl-glycoside
- Quercetin-3-glycoside Rutin
*Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1
**Data on file with WholisticMatters. Values subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Lloyd CM, Marsland BJ. Lung Homeostasis: Influence of Age, Microbes, and the Immune System. Immunity. 2017;46(4):549-61. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.005.
Ramabulana, T., Mavunda, R. D., Steenkamp, P. A., Piater, L. A., Dubery, I. A., & Madala, N. E. (2015). Secondary metabolite perturbations in Phaseolus vulgaris leaves due to gamma radiation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 97, 287-295. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.10.018
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content.
Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.

