Alfalfa: Whole Food Profile
The alfalfa plant (Medicago sativa Linn.) is grown for its unique blend of protein, B vitamins, and minerals. It is a perennial flowering legume widely grown across the world. The sprouts and whole plant material can be used to deliver essential nutrients and phytoactive compounds.
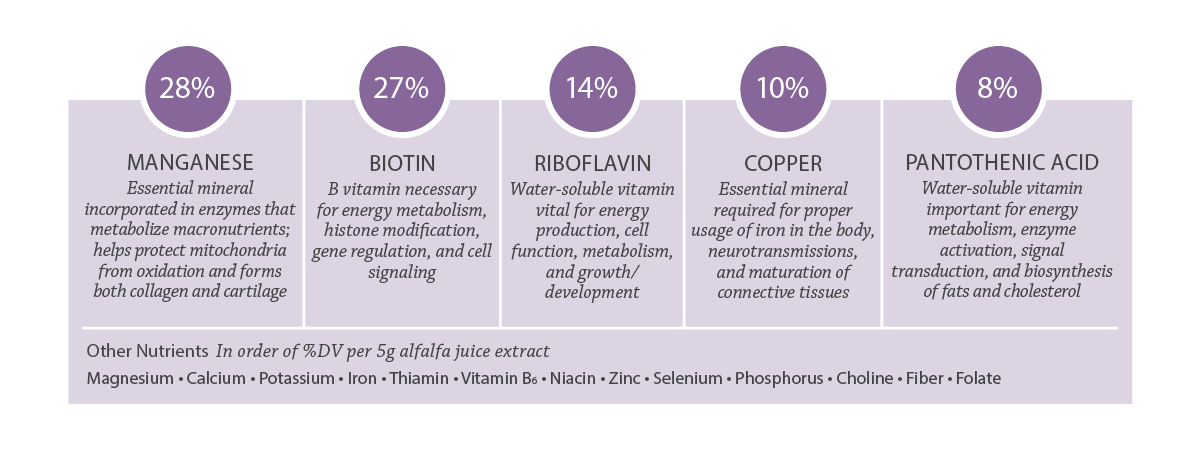
Key Nutrients in Alfalfa
Percentages shown as %DV per serving of 5g alfalfa juice extract.
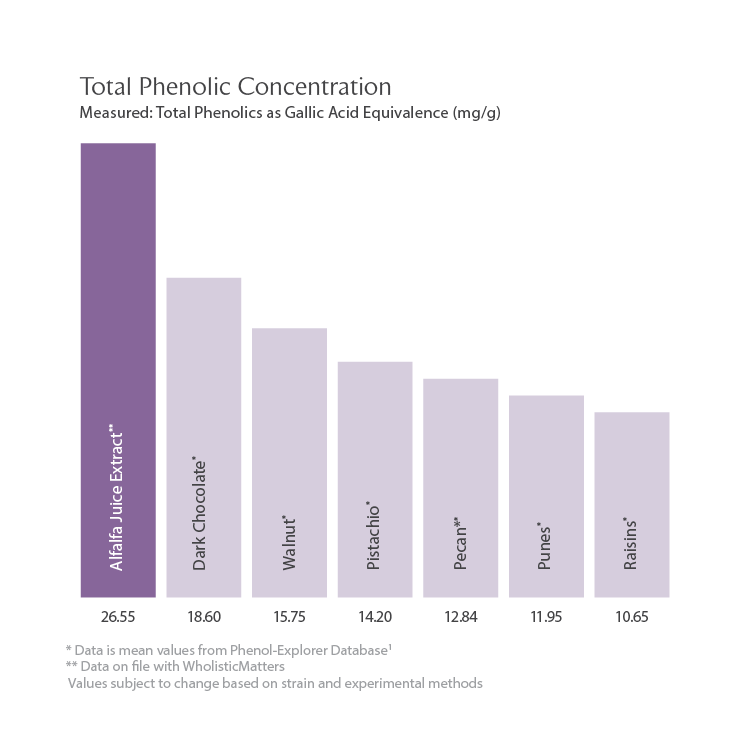
Total Phenolic Concentration in Alfalfa
Measured: Total Phenolics as Gallic Acid Equivalence (mg/g).
Phytoactives in Alfalfa
Flavones
Compounds with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-cancer activity
- Adenosine
- Apigenin
- Luteolin
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants with potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-bacterial activity
Carotenoids
Antioxidants with anti-cancer potential and may lower risk of macular degeneration
- Beta-carotene (0.87 mg/g)*
- Alpha-carotene (0.06 mg/g)*
- Beta Cryptoxanthin (0.06 mg/g)*
Saponins
Support the immune system, healthy cholesterol levels, and blood glucose levels
- Bayogenin
- Foumononetin
- Hederagenin
- Medicagenic Acid
- Soyasapogenol A
- Soyasapogenol B
- Soyasapogenol E
- Soyasaponin I
- Zahnic Acid
Flavonols
Promote antioxidant activity and vascular health
- Quercetin (17 mcg/g)*
*Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1
**Data on file with WholisticMatters. Values subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Bora, K.S. and A. Sharma, Phytochemical and pharmacological potential of Medicago sativa: a review. Pharm Biol, 2011. 49(2): p. 211-20.
Rafinska, K., et al., Medicago sativa as a source of secondary metabolites for agriculture and pharmaceutical industry. Phytochemistry Letters, 2017. 20: p. 520-539.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.
Stochmal, A., et al., Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Flavonoids. 1. Apigenin and Luteolin Glycosides from Aerial Parts. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2001. 49(2): p. 753-758.

