Unfolding Fatty Acids
About this PDF
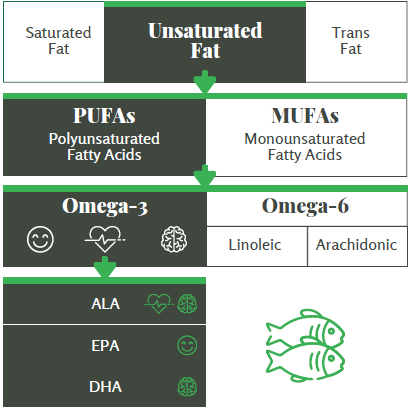
Unsaturated fatty acids can be polyunsaturated (PUFAs) or monounsaturated (MUFAs), indicating the number of double bonds present. These double bonds change the properties of unsaturated fatty acids and contribute to their beneficial effects. Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of PUFA which exert several protective effects in humans, including contributing to heart health, brain health, and the improvement of mood disorders.
Three important omega-3 fatty acids are:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Eicosopentaenoic acid (EPA)
Specifically, ALA contributes to heart health and brain health, while EPA is important in mood disorders. DHA is specifically enriched in the brain and is vital to brain health. Omega-3 fatty acids are found in fish and other seafood, but dietary intake typically falls well below the dose required to achieve the beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acids. Furthermore, ALA is converted to EPA and DHA, the end-product, but conversion is inefficient with only 15 percent of ALA being converted to DHA. Consuming adequate levels of ALA, EPA, and DHA as part of a balanced diet may help ensure optimal functioning of the heart and brain.