The Importance of Liver Health
Summary
The liver has a role in carbohydrate metabolism, blood glucose balance, and lipoprotein synthesis and metabolism. Maintaining a healthy liver reduces risk of diabetes and other diseases.
The liver plays an important role in carbohydrate metabolism, balancing blood glucose levels, and lipoprotein synthesis and metabolism, making liver health quite important.1
Balance of Blood Glucose Levels
When the body does not need glucose for energy, the liver stores it in the form of glycogen.2 The liver is also responsible for synthesis of glucose from fat and protein, and the liver balances blood glucose levels by responding to changing insulin levels:2
- Reserves glucose by converting it to glycogen for storage when insulin levels increase
- Utilizes stored glucose (in the form of glycogen) when insulin levels decrease
Lipoprotein Synthesis and Metabolism
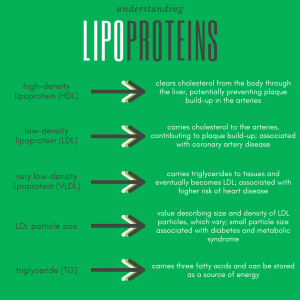
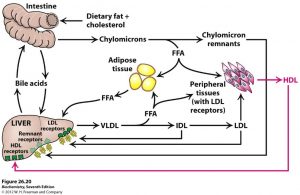
- Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) are synthesized and secreted by the liver.
- VLDL deliver energy-rich triacylglycerol (TAG) to cells in the body.
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) delivers cholesterol to cells in the body.
- HDL is involved in reverse cholesterol transport by bringing back excess cholesterol from cells to the liver for elimination.
- The liver removes cholesterol from the body by converting it to bile salts and putting it into the bile where it can be eliminated in the feces.
Current National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) guidelines suggest standard lipid measurements be used to assess risk for coronary heart disease (CHD) in healthy and diseased populations.3 A “non-HDL cholesterol” lab test result reflects levels of all of major lipoproteins linked with a higher risk of heart disease.2 Non-HDL cholesterol is calculated as total cholesterol (including HDL, LDL, and VLDL but not relying on a triglyceride value) minus HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol).
How Does Impaired Liver Functioning Affect Health?
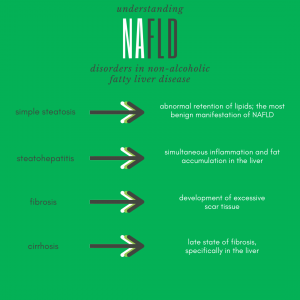
A dysfunctional liver fails to adequately regulate metabolic homeostasis of glucose, usually as a result of insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance and elevated levels of insulin in the blood (compared to corresponding glucose levels) are key factors in the relationship between diabetes and liver disease. Metabolic syndrome is a risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease which is frequently associated with type 2 diabetes.1 Maintaining a healthy liver is important for reducing your risk of these diabetes-associated conditions as well as improving overall glucose homeostasis and optimizing lipoprotein metabolism.
- Garcia-Compean, D., et al. (2009). Liver cirrhosis and diabetes: risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical implications and management. World journal of gastroenterology, 15(3): p. 280-288.
- Kulina, G.R. & Rayfield, E.J. (2016). The role of glucagon in the pathophysiology and management of diabetes. Endocr Pract, 22(5): p. 612-21.
- Third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. (2002). Circulation, 106(25): p. 3143-421.