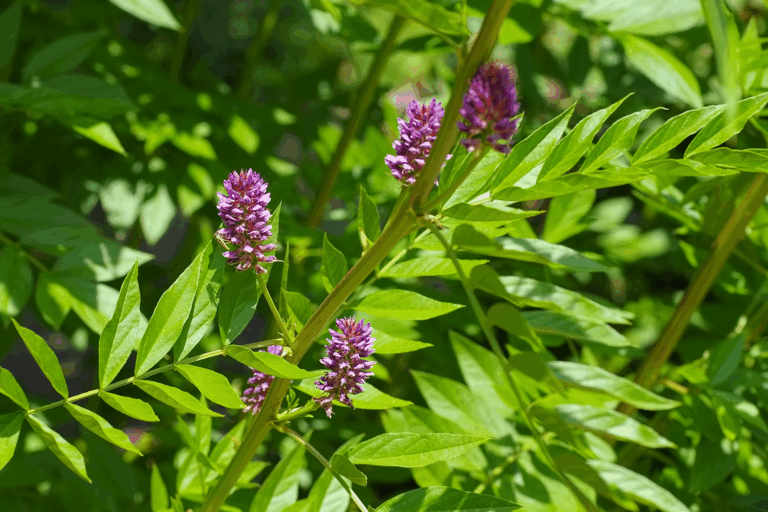
Scientific name:Gymnema sylvestre
Constituents:
- Triterpenoid Saponins (gymnemic acids I-XVIII & gymnemasaponins I-V)
- Polypeptides: gurmarin
- Cyclitol: quercitol
- Phytosterols: stigmasterol
- Amino acid derivatives: betaine, choline & trimethylamine
- Resin
Medicinal actions:
- Astringent
- Bitter
- Diuretic
- Hypoglycemic & Antidiabetic
- Hypocholesterolemic
Mechanism of Action & Pharmacology:
- Triterpene saponins, gymnemic acids, gymnemasaponins, and gurmarin appear to be responsible for sweet suppression and pharmacological effects.
- (Note: Some gymnemic acids are acylate, while the gymnemasaponins are non-acylated, and cylation affects pharmacological activity. Also, gurmarin is active on rodent sweet taste receptors but not on that of humans).
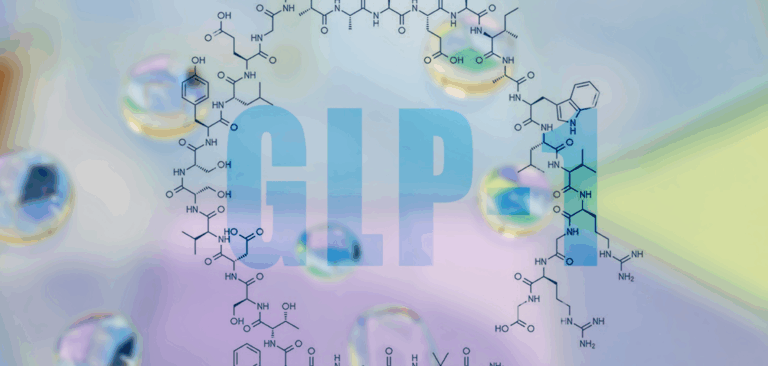
- Anti-diabetic & hypoglycemic activity may be due to a combination of mechanisms, including inhibition of glucose absorption in the small intestine, enhanced endogenous insulin production (possibly by pancreatic regeneration), increases to the activity of enzymes responsible for glucose uptake and utilization (e.g. phosphorylase, gluconeogenic enzymes & sorbitol dehydrogenase), and inhibition of peripheral utilization of glucose by somatotrophin and corticotrophin.
- In one study, gymnemoside b and gymnemic acids III, V and VII produced some inhibitory activity on glucose absorption after oral glucose loading in rats, but gymnemic acid I and gymnemasaponin V were inactive.
Pharmacy:
- Tincture
- Capsules
- As food, fresh juice or infusion
Safety & Toxicity Concerns:
- May cause mild stomach upset and hypoglycemia.
- Safety in pregnancy has not been established.
- No significant adverse effects have been reported, aside from the expected hypoglycemia. Safety in pregnancy has not been established.
- No known contraindications.
Interactions:
- Potential additive effect with other anti-diabetic agents. Prescribe cautiously and monitor blood sugar regularly. Warn patient about possible hypoglycemic effects.