Beetroot: Whole Food Profile
Red table beets (Beta vulgaris var. rubra L.) are the deep red root vegetable loaded with complex carbohydrates, unique phytoactive compounds, essential vitamins, and essential minerals.
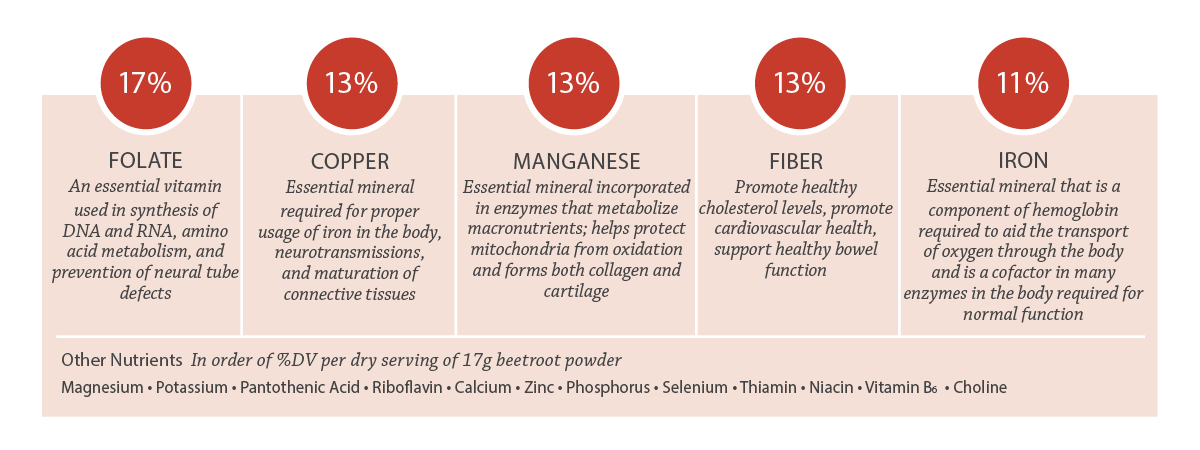
Key Nutrients in Beetroot
Percentages shown as %DV per dry serving of 17g beetroot powder.
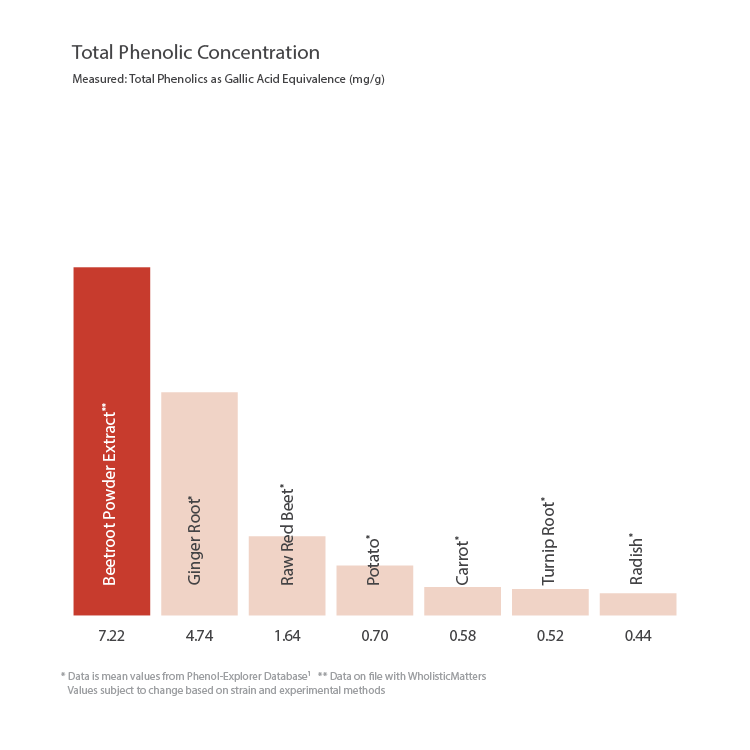
Total Phenolic Concentration in Beetroot
Measured: Total Phenolics as Gallic Acid Equivalence (mg/g).
Phytoactives in Beetroot
Flavones
Compounds with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-cancer activity
- Luteolin (3.7 mcg/g)*
Nitrate
Supports exercise performance and cardiovascular health
Betalains
Natural pigments with antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-lipidemic, and antimicrobial properties
Fiber
Supports cardiovascular health, healthy bowel function, and healthy cholesterol levels
- Arabinoxylan
Lignans
Cross-linked phenolic compounds that make up plant cell walls and are insoluble fibers that aid in fecal bulking and feed some gut bacteria
- Secoisolariciresinol (0.07 mcg/g)*
Flavonols
Promote antioxidant activity and vascular health
- Quercetin(1.3 mcg/g)*
*Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1
**Data on file with WholisticMatters. Values subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Clifford, T., et al., The potential benefits of red beetroot supplementation in health and disease. Nutrients, 2015. 7(4): p. 2801-2822.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.

