Buckwheat: Whole Food Profile
The common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) plant is a pseudo-cereal grown for its unique ability to out-compete other plants for sun, soil, and water. It packs these nutrients into leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. The fruits are a grain-like staple, and juice from the plant material contains essential nutrients and bioactive compounds.
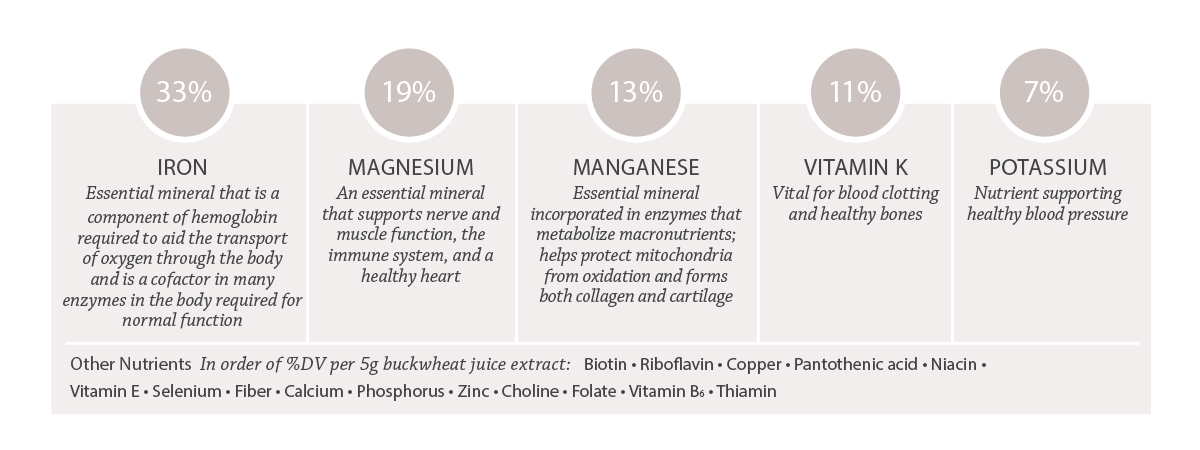
Key Nutrients in Buckwheat
Percentages shown as %DV per serving of 5g buckwheat juice extract.
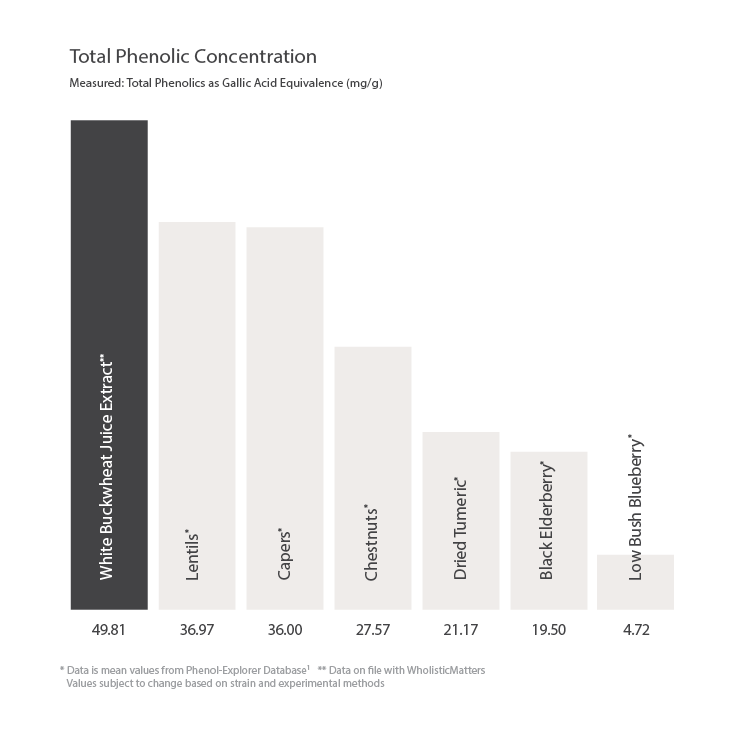
Total Phenolic Concentration in Buckwheat
Measured: Total Phenolics as Gallic Acid Equivalence (mg/g).
Phytoactives in Buckwheat
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants with potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-bacterial activity
Carotenoids
Antioxidants with anti-cancer potential and may lower risk of macular degeneration
- Beta-carotene (52.26 mg/g)*
- Lutein(0.06 mg/g)*
- Zeaxanthin (0.06 mg/g)*
Anthocyanidins
Purple and red pigments concentrated in buckwheat stems with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity
- Cyanidin-3-galactoside(11.1 mcg/g)**
- Cyanidin-3-glucoside(5.3 mcg/g)**
- Cyanidin (0.1 mcg/g)**
Flavonols
Promote antioxidant activity and vascular health
- Rutin (12 mcg/g)*
- Quercetin(17 mcg/g)*
*Data is mean values from Phenol-Explorer Database1
**Data on file with WholisticMatters. Values subject to change based on strain and experimental methods
Did you know WholisticMatters is powered by Standard Process? Learn more about Standard Process’ whole food-based nutrition philosophy.
Rothwell, J.A., et al., Phenol-Explorer 3.0: a major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database, 2013. 2013: p. bat070-bat070.

